一、接口请求方法
1.1 简介
- 接口请求方法是指在进行应用程序编程接口(API)通信时,使用的HTTP方法。
- HTTP方法定义了客户端与服务器之间通信的目的和操作类型。
1.2 常见的HTTP请求方法
| 方法 |
含义 |
描述 |
| GET |
获取 |
用于从服务器获取资源。 |
| POST |
提交 |
用于将数据提交到服务器,以创建新的资源。 |
| PUT |
更新 |
用于更新服务器上的资源,或者创建新的资源(若不存在)。 |
| DELETE |
删除 |
用于请求服务器删除指定的资源。 |
- 这些HTTP方法提供了在客户端和服务器之间,进行通信的灵活性和标准化,使开发人员能够根据不同的操作,要求选择合适的方法。
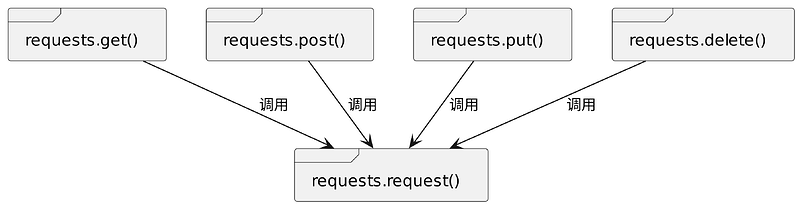
1.3 常见HTTP请求方法构造
| 方法 |
说明 |
| requests.request() |
构造一个请求,支撑以下各方法的基础方法。 |
| requests.get() |
构造HTTP协议中的GET请求。 |
| requests.post() |
构造HTTP协议中的POST请求。 |
| requests.put() |
构造HTTP协议中的PUT请求。 |
| requests.delete() |
构造HTTP协议中的DELETE请求。 |
1.4 实战
1.4.1 构造GET请求
-
requests.get(url, params=None, **kwargs)
- url:拼接url;
- params:拼接在url中的请求参数;
- **kwargs:更多底层支持的参数。
# 导入依赖
import requests
def test_get():
# 定义接口的 url 和拼接在 url 中的请求参数
url = "https://httpbin.ceshiren.com/get"
# 发出 GET 请求,r 接收接口响应
r = requests.get(url)
# 打印接口响应
logger.info(f"接口响应为 {r}")
1.4.2 构造POST请求
-
requests.post(url, data=None, json=None, **kwargs)
- data:表单格式请求体;
- json:JSON格式请求体。
# 导入依赖
import requests
def test_post():
# 定义接口的 url
url = "https://httpbin.ceshiren.com/post"
# 发出 POST 请求,r 接收接口响应
r = requests.post(url)
# 打印接口响应
logger.info(f"接口响应为 {r}")
1.4.3 构造PUT请求
requests.put(url, data=None, **kwargs)
# 导入依赖
import requests
def test_put():
# 定义接口的 url
url = "https://httpbin.ceshiren.com/put"
# 发出 POST 请求,r 接收接口响应
r = requests.put(url)
# 打印接口响应
logger.info(f"接口响应为 {r}")
1.4.4 构造DELETE请求
requests.delete(url, ** kwargs)
# 导入依赖
import requests
def test_delete():
# 定义接口的 url 和表单格式请求体
url = "https://httpbin.ceshiren.com/delete"
# 发出 POST 请求,r 接收接口响应
r = requests.delete(url)
# 打印接口响应
logger.info(f"接口响应为 {r}")
1.4.5 构造请求方法
-
requests.request(method, url, **kwargs)
- method:请求方法。
- GET,OPTIONS,HEAD,POST,PUT,PATCH,DELETE。
def request(method, url, **kwargs):
"""Constructs and sends a :class:`Request <Request>`.
:param method: method for the new :class:`Request` object: ``GET``, ``OPTIONS``, ``HEAD``, ``POST``, ``PUT``, ``PATCH``, or ``DELETE``.
:param url: URL for the new :class:`Request` object.
:param params: (optional) Dictionary, list of tuples or bytes to send
in the query string for the :class:`Request`.
:param data: (optional) Dictionary, list of tuples, bytes, or file-like
object to send in the body of the :class:`Request`.
:param json: (optional) A JSON serializable Python object to send in the body of the :class:`Request`.
:param headers: (optional) Dictionary of HTTP Headers to send with the :class:`Request`.
:param cookies: (optional) Dict or CookieJar object to send with the :class:`Request`.
:param files: (optional) Dictionary of ``'name': file-like-objects`` (or ``{'name': file-tuple}``) for multipart encoding upload.
``file-tuple`` can be a 2-tuple ``('filename', fileobj)``, 3-tuple ``('filename', fileobj, 'content_type')``
or a 4-tuple ``('filename', fileobj, 'content_type', custom_headers)``, where ``'content-type'`` is a string
defining the content type of the given file and ``custom_headers`` a dict-like object containing additional headers
to add for the file.
:param auth: (optional) Auth tuple to enable Basic/Digest/Custom HTTP Auth.
:param timeout: (optional) How many seconds to wait for the server to send data
before giving up, as a float, or a :ref:`(connect timeout, read
timeout) <timeouts>` tuple.
:type timeout: float or tuple
:param allow_redirects: (optional) Boolean. Enable/disable GET/OPTIONS/POST/PUT/PATCH/DELETE/HEAD redirection. Defaults to ``True``.
:type allow_redirects: bool
:param proxies: (optional) Dictionary mapping protocol to the URL of the proxy.
:param verify: (optional) Either a boolean, in which case it controls whether we verify
the server's TLS certificate, or a string, in which case it must be a path
to a CA bundle to use. Defaults to ``True``.
:param stream: (optional) if ``False``, the response content will be immediately downloaded.
:param cert: (optional) if String, path to ssl client cert file (.pem). If Tuple, ('cert', 'key') pair.
:return: :class:`Response <Response>` object
:rtype: requests.Response
1.4.6 底层参数说明
| 参数 |
应用场景 |
| method |
请求方法 |
| url |
请求URL |
| params |
请求中携带URL参数 |
| data |
请求中携带请求体(默认为表单请求) |
| JSON |
请求中携带JSON格式的请求体 |
| headers |
请求中携带头信息 |
| cookies |
请求中携带cookies |
| files |
请求中携带文件格式的请求体 |
| auth |
请求中携带认证信息 |
| timeout |
设置请求超时时间 |
| allow_redirects |
设置是否允许重定向 |
| proxies |
设置请求代理 |
| verify |
请求是否要认证 |
| cert |
请求中携带ssl证书 |
二、接口请求参数
2.1 请求参数简介
2.2 携带请求参数的方式
- 常用两种方式:
- 直接在URL中拼接:
?username=Hogwarts&id=666
- 通过params传递参数:
requests.get(url, params)
2.2.1 携带请求参数的GET请求
# 导入依赖
import requests
def test_get_by_params():
# 定义接口的 url 和拼接在 url 中的请求参数
url = "https://httpbin.ceshiren.com/get"
params ={
"get_key": "get_value"
}
# 发出 GET 请求,r 接收接口响应
r = requests.get(url, params=params)
def test_get_by_url():
# 定义接口的 url 和拼接在 url 中的请求参数
url = "https://httpbin.ceshiren.com/get?get_key=get_value"
# 发出 GET 请求,r 接收接口响应
r = requests.get(url)
2.2.2 携带请求参数的POST请求
# 导入依赖
import requests
def test_post_by_params():
# 定义接口的 url 和表单格式请求体
url = "https://httpbin.ceshiren.com/post"
params = {
"post_key": "post_value"
}
# 发出 POST 请求,r 接收接口响应
r = requests.post(url, params=params)
三、接口请求头
3.1 请求头信息的使用场景
3.2 请求头信息
- HTTP请求头是在HTTP请求信息中包含的元数据信息,用于描述请求或响应的一些属性和特征。
- 实际工作过程中具体要关注的头信息字段需要和研发沟通。
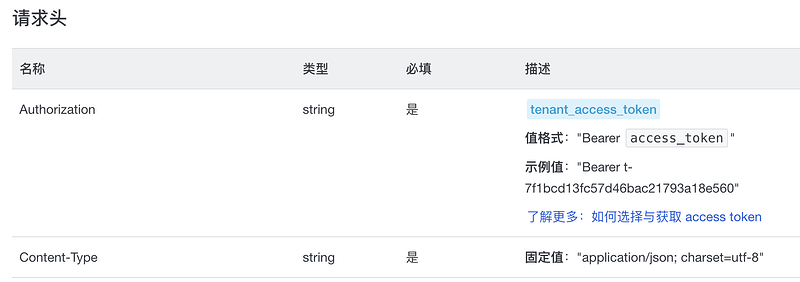
- 常见的头信息:
| 内容 |
含义 |
| Authorization |
表示客户端请求的身份验证信息 |
| Cookie |
表示客户端的状态信息,通常用于身份验证和会话管理 |
| Content-Type |
表示请求消息体的MIME类型 |
| User-Agent |
发送请求的客户端软件信息 |
2.3 构造头信息
headers = {'user-agent': 'my-app/0.0.1'}
r = requests.get(url, headers=headers)
四、接口请求体-JSON
4.1 接口请求体
- 进行HTTP请求时,发送给服务器的数据;
- 数据格式类型可以是JSON、XML、文本、图像等格式;
- 请求体的格式和内容取决于服务端API的设计和开发人员的要求。
4.2.1 常用接口请求体
| 类型 |
介绍 |
Content-type |
| JSON(JavaScript Object Notation) |
轻量级的数据交换格式,最常见的一种类型。 |
application/json |
| 表单数据(Form Data) |
以键值对的形式提交数据,例如通过HTML表单提交数据。 |
application/x-www-form-urlencoded |
| XML(eXtensible Markup Language) |
常用的标记语言,通常用于传递配置文件等数据。 |
application/xml text/xml |
| 文件(File) |
可以通过请求体上传文件数据,例如上传图片、视频等文件。 |
上传文件的MIME类型,如image/jpeg multipart/form-data |
| 纯文本(Text) |
纯文本数据,例如发送邮件、发送短信等场景。 |
text/plain |
| 其他格式 |
二进制数据、protobuf等格式。 |
|
4.2 JSON格式请求体介绍
4.2.1 JSON简介
- 是JavaScript Object Notation缩写;
- 是一种轻量级的数据交换格式;
- 是理想的接口数据交换语言;
- Content-type为application/json。
4.2.2 JSON格式请求体示例
- 进入登录页面;
- 打开开发者工具;
- 输入用户名密码,点击登录。
练习地址:https://litemall.hogwarts.ceshiren.com/#/login
4.3 如何构造JSON格式请求体
# 导入依赖
import requests
def test_post_json():
# 定义接口的 url 和 json 格式请求体
url = "https://httpbin.ceshiren.com/post"
params = {
"post_key": "post_value"
}
# 发出 POST 请求,r 接收接口响应
r = requests.post(url, json=params)
五、接口响应断言
5.1 接口断言使用场景
- 问题:
-
- 如何确保请求可以发送成功。
-
- 如何保证符合业务需求。
- 解决方案:
- 通过获取响应信息,验证接口请求是否成功,是否符合业务需求。
5.2 Requests中的响应结果对象
import requests
from requests import Response
# Response就是一个响应对象
r: Response = requests.get('http://www.example.com')
5.2.1 响应结果类型
| 属性 |
含义 |
| r |
响应Response对象(可以使用任意的变量名)。 |
| r.status_code |
HTTP响应状态码。 |
| r.headers |
返回一个字段,包含响应头的所有信息。 |
| r.text |
返回响应的内容,是一个字符串。 |
| r.url |
编码之后的请求的url。 |
| r.content |
返回响应的内容,是一个字节流。 |
| r.raw |
响应的原始内容。 |
| r.json() |
如果响应的内容是JSON格式,可以使用该
方法将其解析成Python对象。 |
# 导入依赖
import requests
def test_res_assert():
# 定义接口的 url 和 json 格式请求体
url = "https://httpbin.ceshiren.com/get"
# 发出 GET 请求,r 接收接口响应
r = requests.post(url)
5.3 响应结果断言
import requests
def test_req():
r = requests.get("https://httpbin.ceshiren.com/get")
assert r.status_code == 200
六、JSON响应体断言
6.1 JSON响应体简介
- JSON格式的响应体,是指HTTP响应中的消息体(message body),它是以JSON格式编码的数据。
{
"name": "John",
"age": 30,
"city": "New York"
}
6.2 断言JSON格式响应体的使用场景
6.3 断言JSON格式响应体
import requests
def test_res_json():
r = requests.get("https://httpbin.ceshiren.com/get")
assert r.status_code == 200
assert r.json()["url"] == "https://httpbin.ceshiren.com/get"
6.4 遇到复杂断言该如何处理
- 多层嵌套的数据提取与断言:JSONPath
- 整体结构响应断言:JSONSchema
- 自行编写解析算法。