一、Allure2的用法
| 方法名 | 方法参数 | 参数说明 |
|---|---|---|
@allure.epic() |
epic描述 | 在敏捷开发中,史诗(epic)是较大的用户需求或项目目标。在史诗之下可以有多个功能点(feature) |
@allure.feature() |
模块名称 | 功能点的描述,通常代表一个特定的功能模块或组件,下面可以有多个有故事(story) |
@allure.story() |
用户故事 | 通常代表一个特定的用户需求或功能场景,下面可以有多个测试用例(testcase) |
@allure.title() |
用例标题 | 用于重命名HTML报告中的测试用例名称,可以为每个测试用例提供一个清晰且描述性强的标题 |
@allure.step() |
操作步骤 | 测试用例的步骤描述,每个步骤可以包含具体的操作和预期结果,便于详细记录测试用例的执行过程 |
@allure.testcase() |
测试用例的链接地址 | 对应功能测试用例系统中的case链接 |
@allure.issue |
缺陷 | 对应缺陷管理系统中的链接,便于追踪缺陷和查看详细信息 |
@allure.description() |
用例描述 | 测试用例的描述,便于理解测试用例的目的和背景 |
@allure.severity() |
用例等级 | blocker,critical,normal,minor,trivial,便于标识测试用例的重要性和优先级 |
@allure.link() |
链接 | 定义一个链接,在测试报告中展现,便于引用外部资源或相关信息 |
@allure.attachment() |
附件 | 报告添加附件,例如截图、日志文件等,便于提供详细的测试结果和上下文信息 |
二、 Allure2报告中添加用例标题
2.1 背景
- 应用场景:
- 为了让生成的测试报告便于阅读,可以为每条用例添加一个便于阅读的标题(可以使用中文标题)。
- 生成的测试报告展示用例时,就会以设置的标题名展示出来。
2.2 方法
-
通过使用装饰器
@allure.title可以为测试用例自定义一个可阅读的标题。 -
allure.title的三种使用方式:-
- 直接使用
@allure.title为测试用例自定义标题;
- 直接使用
-
-
@allure.title支持通过占位符的方式传递参数,可以实现测试用例标题参数化,动态生成测试用例标题;
-
-
-
allure.dynamic.title动态更新测试用例标题。
-
-
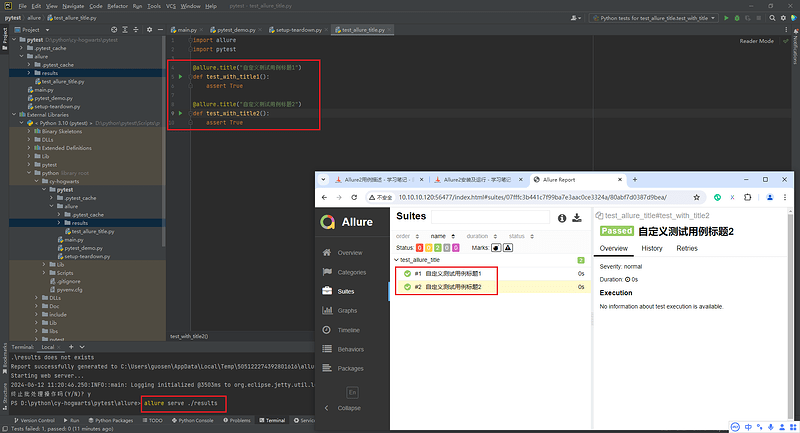
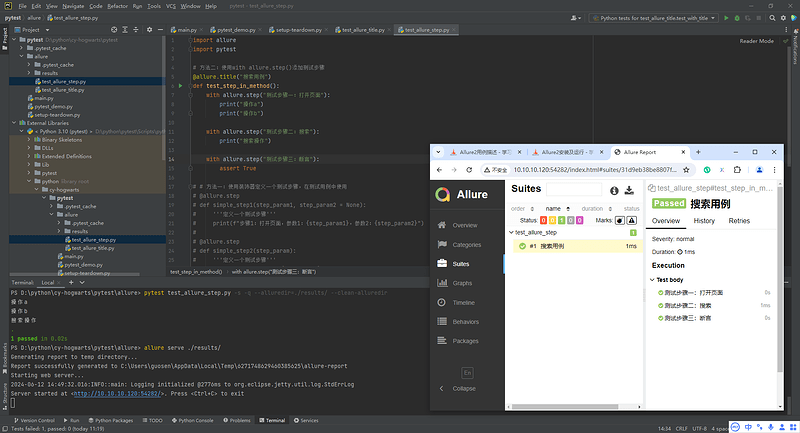
2.2.1 Allure2报告中直接设置用例标题
- 直接使用装饰器:
import allure
import pytest
@allure.title("自定义测试用例标题")
def test_with_title():
assert True
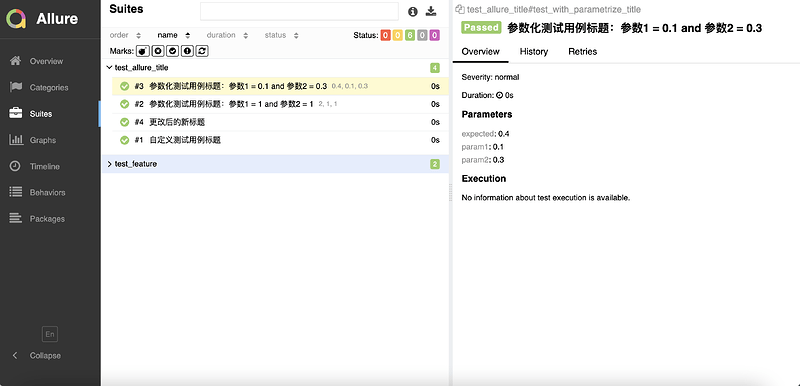
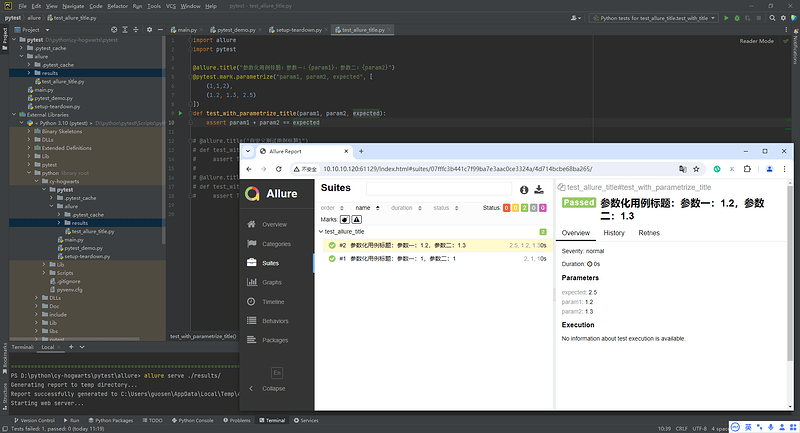
2.2.2 Allure2报告参数化设置用例标题
- 通过占位符的方式传递参数,可以实现测试用例标题参数化,动态生成测试用例标题:
import allure
import pytest
@allure.title("参数化用例标题:参数一:{param1},参数二:{param2}")
@pytest.mark.parametrize("param1, param2, expected",[
(1, 1, 2),
(1.1, 1.2, 1.3)
])
def test_with_parametrize_title(param1, param2, expected):
assert param1 + param2 == expected
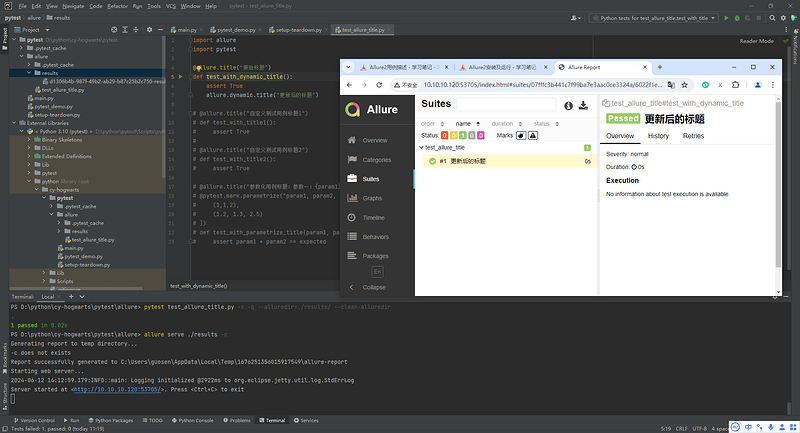
2.2.3 Allure2报告动态更新测试用例标题
- 动态更新测试用例标题:
import allure
import pytest
@allure.title("原始标题")
def test_with_dynamic_title():
assert True
allure.dynamic.title("更改后的新标题")
三、Allure2报告中添加用例步骤
3.1 背景
- 应用场景:
- 编写自动化测试用例时,经常遇到需要编写流程性测试用例的场景,一般流程性的测试用例,测试步骤比较多,我们在测试用例中添加详细的步骤,会提高测试用例的可阅读性。
3.2 方法
- Allure支持两种方法:
- 方法一:使用装饰器定义一个测试步骤,在测试用例中使用;
- 方法二:使用
with allure.step()添加测试步骤。
3.2.1 Allure2报告装饰器添加用例步骤
# 方法一:使用装饰器定义一个测试步骤,在测试用例中使用
import allure
import pytest
@allure.step
def simple_step1(step_param1, step_param2 = None):
'''定义一个测试步骤'''
print(f"步骤1:打开页面,参数1: {step_param1}, 参数2:{step_param2}")
@allure.step
def simple_step2(step_param):
'''定义一个测试步骤'''
print(f"步骤2:完成搜索 {step_param} 功能")
@pytest.mark.parametrize('param1', ["pytest", "allure"], ids=['search pytest', 'search allure'])
def test_parameterize_with_id(param1):
simple_step2(param1)
@pytest.mark.parametrize('param1', [True, False])
@pytest.mark.parametrize('param2', ['value 1', 'value 2'])
def test_parametrize_with_two_parameters(param1, param2):
simple_step1(param1, param2)
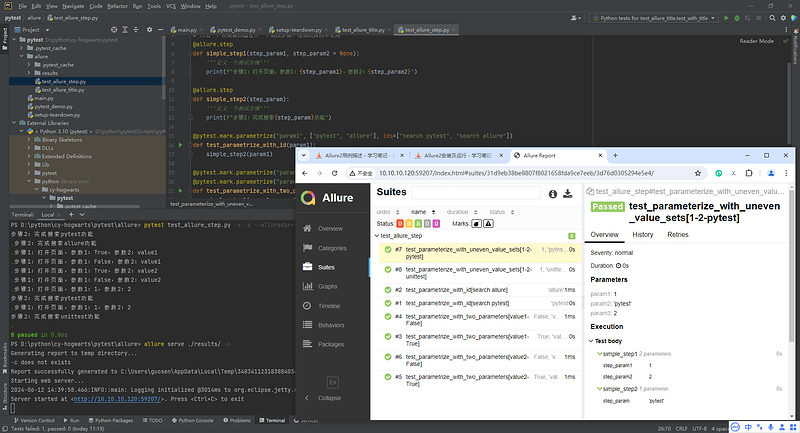
@pytest.mark.parametrize('param2', ['pytest', 'unittest'])
@pytest.mark.parametrize('param1,param3', [[1,2]])
def test_parameterize_with_uneven_value_sets(param1, param2, param3):
simple_step1(param1, param3)
simple_step2(param2)
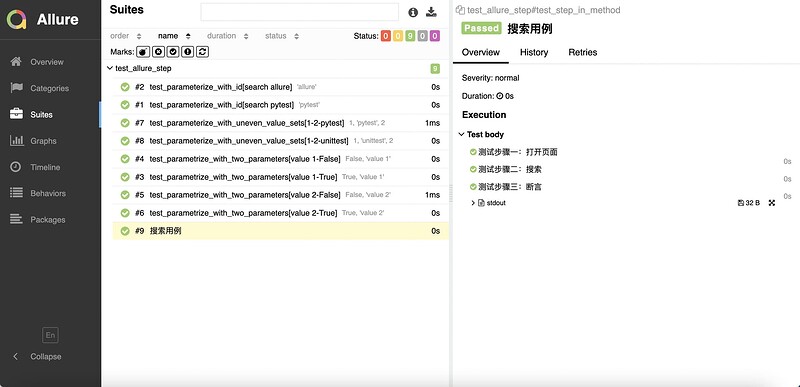
3.2.2 Allure使用with allure.step()添加测试步骤
# 方法二:使用 `with allure.step()` 添加测试步骤
@allure.title("搜索用例")
def test_step_in_method():
with allure.step("测试步骤一:打开页面"):
print("操作 a")
print("操作 b")
with allure.step("测试步骤二:搜索"):
print("搜索操作 ")
with allure.step("测试步骤三:断言"):
assert True
四、Allure1报告中添加用例链接
4.1 背景
- 应用场景:
- 将报告与bug管理系统或测试用例管理系统集成,可以添加链接装饰器``@allure.link
、@allure.issue和@allure.testcase`。
- 将报告与bug管理系统或测试用例管理系统集成,可以添加链接装饰器``@allure.link
4.2 Allure2的用例链接
- 格式 1:
@allure.link(url, name)添加一个普通的 link 链接。 - 格式 2:
@allure.testcase(url, name)添加一个用例管理系统链接。 - 格式 3:
@allure.issue(url, name),添加 bug 管理系统链接。
import allure
import pytest
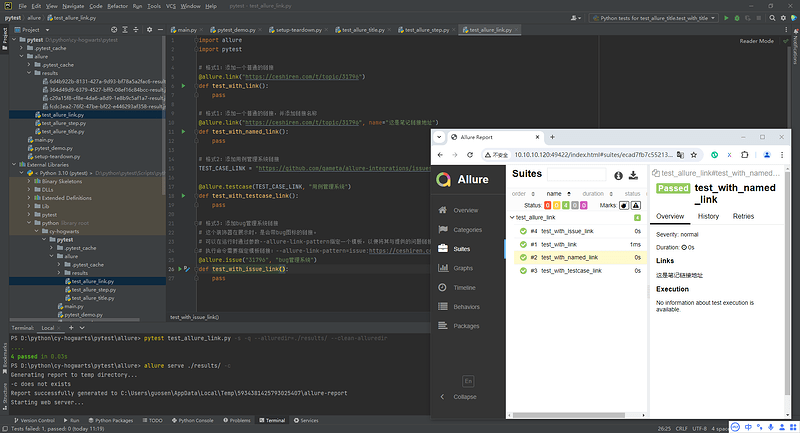
# 格式1:添加一个普通的链接
@allure.link("https://ceshiren.com/t/topic/31796")
def test_with_link():
pass
# 格式1:添加一个普通的链接,并添加链接名称
@allure.link("https://ceshiren.com/t/topic/31796", name="这是笔记链接地址")
def test_with_named_link():
pass
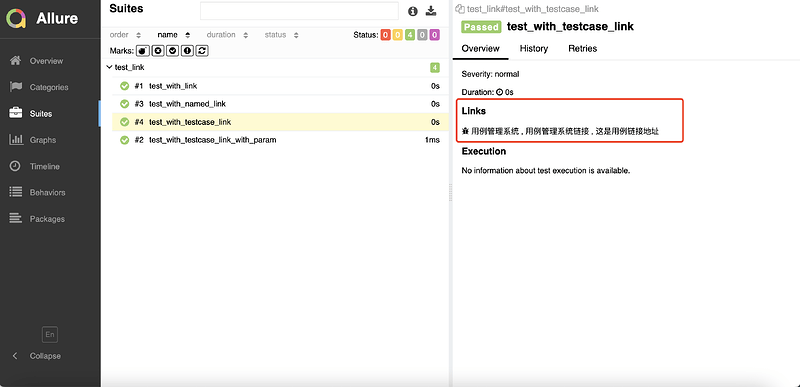
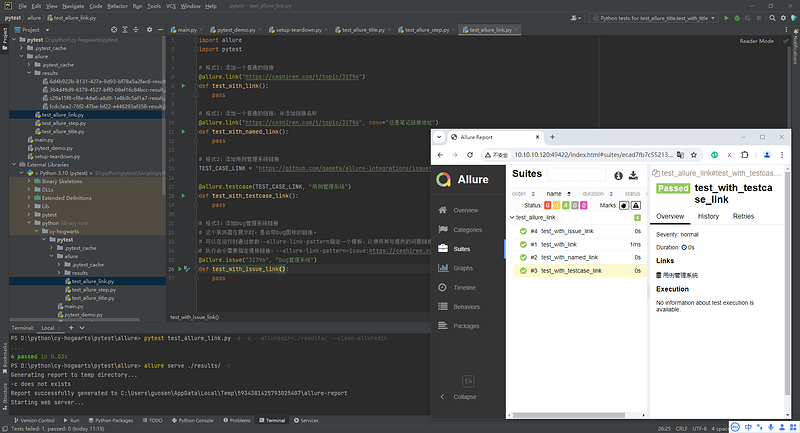
# 格式2:添加用例管理系统链接
TEST_CASE_LINK = "https://github.com/qameta/allure-integrations/issues/8#issuecomment-268313637"
@allure.testcase(TEST_CASE_LINK, "用例管理系统")
def test_with_testcase_link():
pass
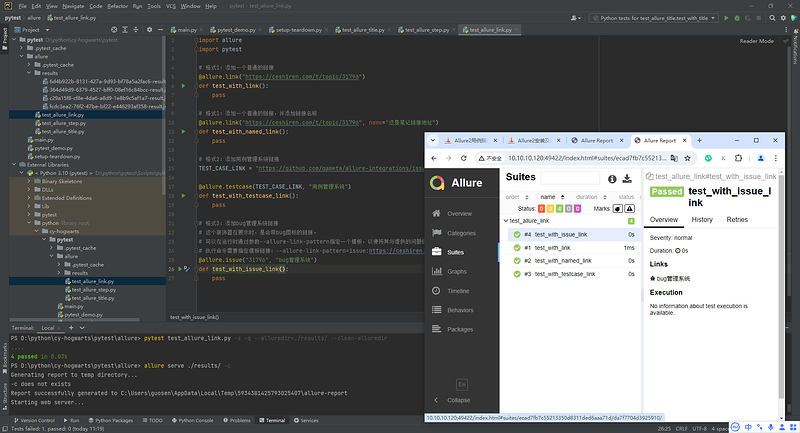
# 格式3:添加bug管理系统链接
# 这个装饰器在展示时,是会带bug图标的链接。
# 可以在运行时通过参数--allure-link-pattern指定一个模板,以便将其与提供的问题链接类型链接模板一起使用。
# 执行命令需要指定模板链接:--allure-link-pattern=issue:https://ceshiren.com/t/topic/{}
@allure.issue("31796", "bug管理系统")
def test_with_issue_link():
pass
五、Allure2报告中添加用例分类
5.1 背景
- 应用场景:
- 可以为项目,以及项目下的不同模块,对用例进行分类管理。也可以运行某个类别下的用例。
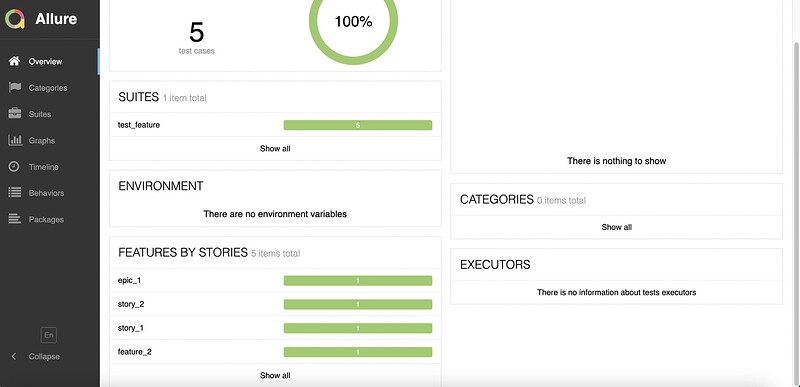
- 报告展示:
- 类别会展示在测试报告的Behaviors栏目下。
5.2 方法
- Allure提供了三个装饰器:
-
@allure.epic:敏捷里的概念,定义史诗,往下是feature。 -
@allure.feature:功能点的描述,理解成模块,往下是story。 -
@allure.story:故事story是feature的子集。
-
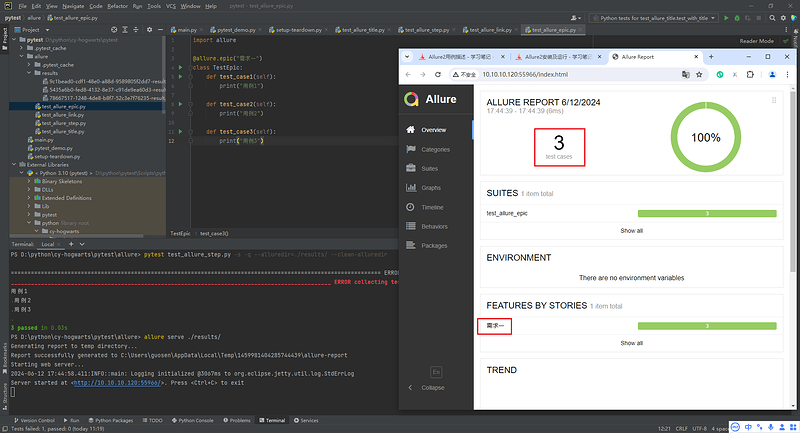
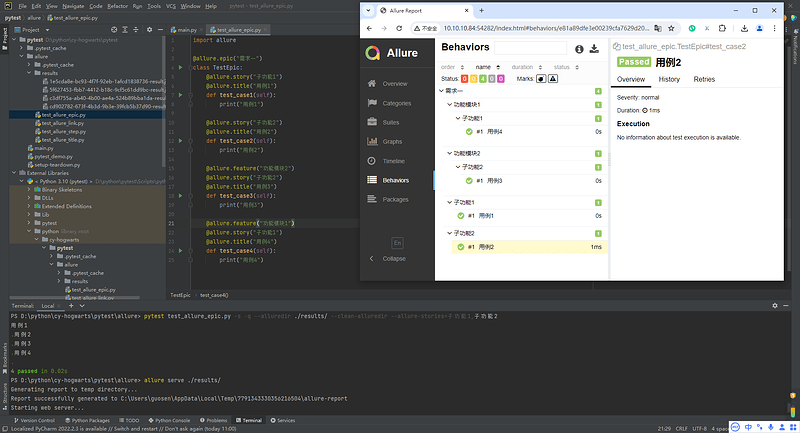
5.3 Allure分类-epic
- 场景:希望在测试报告中看到用例所在的项目,需要用到epic,相当于定义一个项目的需求,由于颗粒度比较大,在epic下还要定义略小粒度的用户故事。
- 解决:
@allure.epic
import allure
@allure.epic("需求1")
class TestEpic:
def test_case1(self):
print("用例1")
def test_case2(self):
print("用例2")
def test_case3(self):
print("用例3")
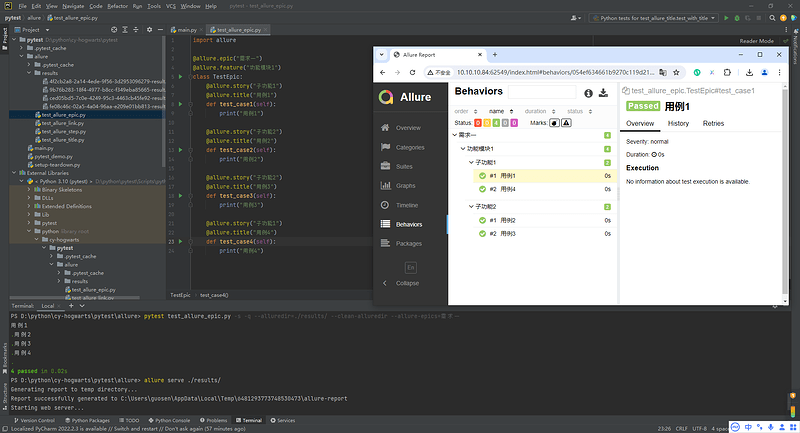
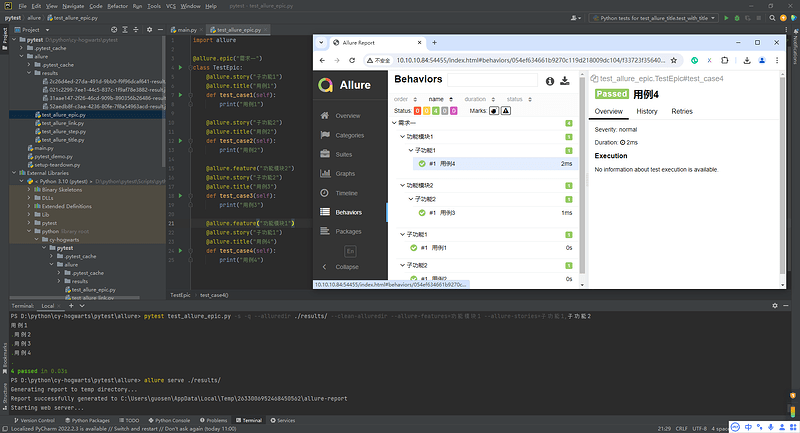
5.4 Allure分类-feature/story
- 场景:希望在报告中看到测试功能,子功能或场景;
- 解决:
@allure.feature、@allure.story - 步骤:
- 功能上加
@allure.feature('功能名称') - 子功能上加
@allure.story('子功能名称')
- 功能上加
import allure
@allure.epic("需求1")
@allure.feature("功能模块1")
class TestEpic:
@allure.story("子功能1")
@allure.title("用例1")
def test_case1(self):
print("用例1")
@allure.story("子功能2")
@allure.title("用例2")
def test_case2(self):
print("用例2")
@allure.story("子功能2")
@allure.title("用例3")
def test_case3(self):
print("用例3")
@allure.story("子功能1")
@allure.title("用例4")
def test_case4(self):
print("用例4")
5.5 Allure运行feature/story
- allure相关的命令查看:
pytest --help|findstr allure
- 通过指定命令行参数,运行epic/feature/story相关的用例:
pytest 文件名 --allure-epics=EPICS_SET --allure-features=FEATURES_SET --allure-stories=STORIES_SET
# 只运行 epic 名为 "需求1" 的测试用例
pytest --alluredir ./results --clean-alluredir --allure-epics=需求1
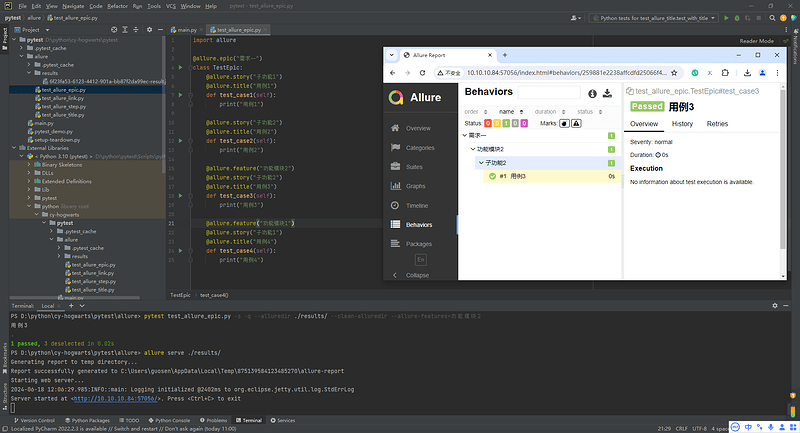
# 只运行 feature 名为 "功能模块2" 的测试用例
pytest --alluredir ./results --clean-alluredir --allure-features=功能模块2
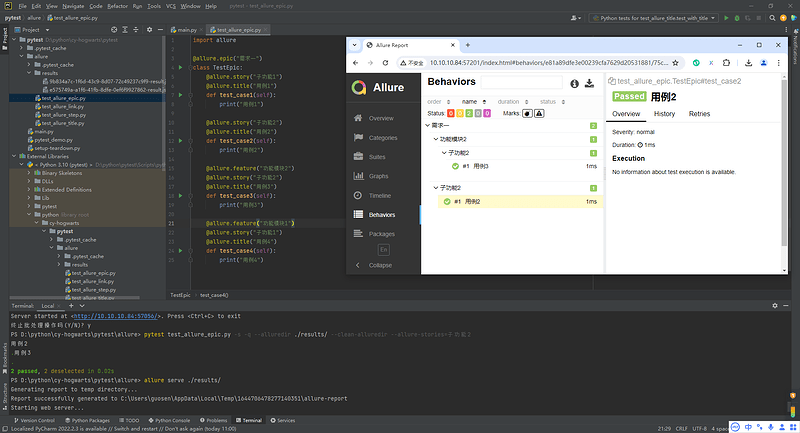
# 只运行 story 名为 "子功能2" 的测试用例
pytest --alluredir ./results --clean-alluredir --allure-stories=子功能2
# 运行 story 名为 "子功能1和子功能2" 的测试用例
pytest --alluredir ./results --clean-alluredir --allure-stories=子功能1,子功能2
# 运行 feature + story 的用例(取并集)
pytest --alluredir ./results --clean-alluredir --allure-features=功能模块1 --allure-stories=子功能1,子功能2
5.6 Allure epic/feature/story的关系
- epic:敏捷里的概念,用来定义史诗,相当于定义一个项目;
- feature:相当于一个功能模块,相当于test suite,可以管理很多个子分支story;
- story:相当于对应这个功能或者模块下的不同场景,分支功能;
- epic与feature、feature与story类似于父子关系。
六、Allure报告中添加用例描述
6.1 背景
-
应用场景:
- Allure支持往测试报告中对测试用例添加非常详细的描述语,用来描述测试用例详情。
-
Allure添加描述的四种方式:
- 方式一:使用装饰器
@allure.description()传递一个字符串参数来描述测试用例; - 方式二:使用装饰器
@allure.description_html()传递一段HTML文本来描述测试用例; - 方式三:直接在测试用例方法中,通过编写文档注释的方法,来添加描述;
- 方法四:用例代码内部动态添加描述信息。
- 方式一:使用装饰器
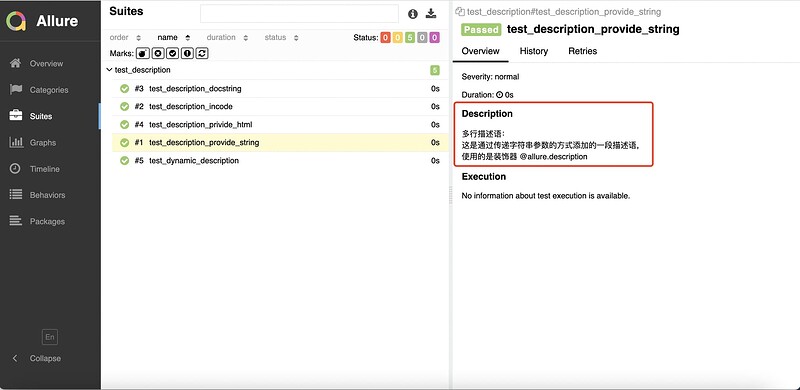
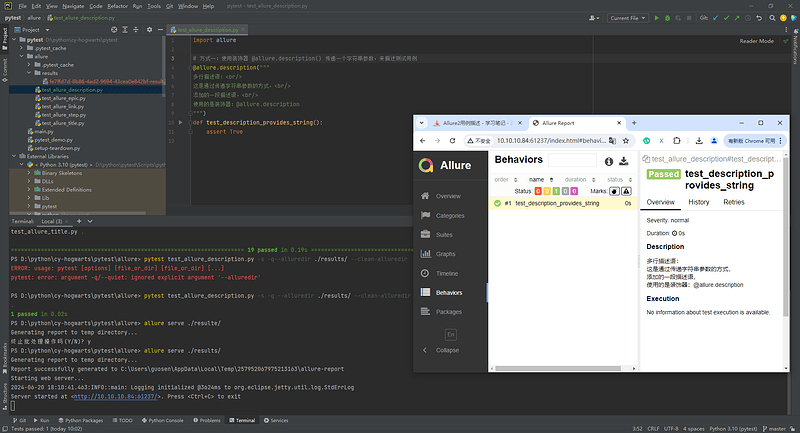
6.2 添加装饰器@allure.description()
import allure
# 方式一:使用装饰器 @allure.description() 传递一个字符串参数,来描述测试用例
@allure.description("""
多行描述语:<br/>
这是通过传递字符串参数的方式,<br/>
添加的一段描述语,<br/>
使用的是装饰器:@allure.description
""")
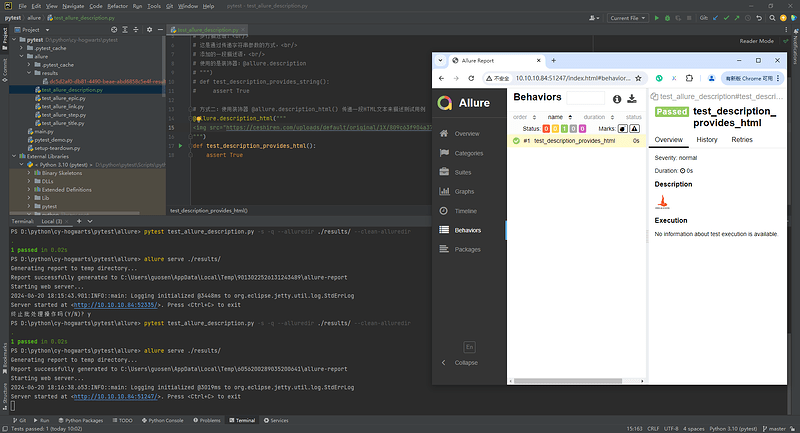
def test_description_provides_string():
assert True
6.3 添加装饰器@allure.description_html()
# 方式二:使用装饰器 @allure.description_html() 传递一段HTML文本来描述测试用例
@allure.description_html("""
<img src="https://ceshiren.com/uploads/default/original/1X/809c63f904a37bc0c6f029bbaf4903c27f03ea8a.png" width="36" alt="测试人社区" id="site-logo" class="logo-small">
""")
def test_description_provides_html():
assert True
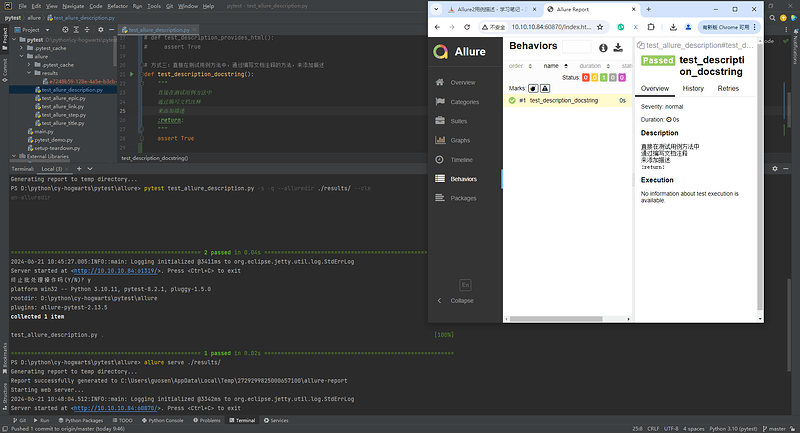
6.4 直接在代码中添加文档注释
def test_description_docstring():
"""
直接在测试用例方法中 </br>
通过编写文档注释的方法 </br>
来添加描述。 </br>
:return:
"""
assert True
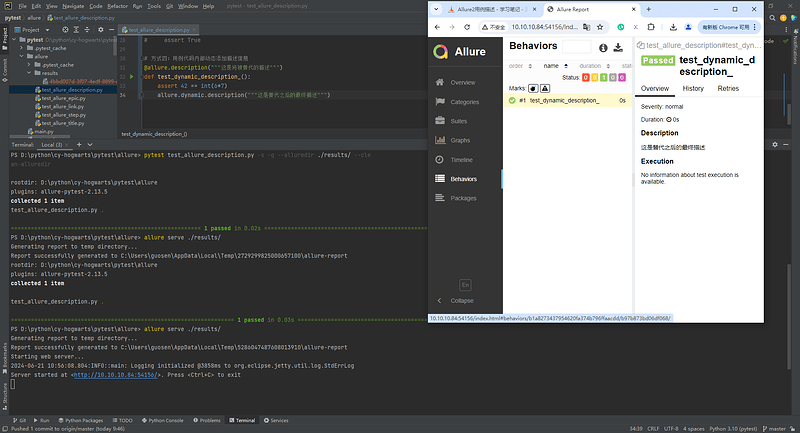
6.5 代码中添加动态描述信息
import allure
@allure.description("""这个描述将被替换""")
def test_dynamic_description():
assert 42 == int(6 * 7)
allure.dynamic.description("这是最终的描述信息")
# allure.dynamic.description_html(''' html 代码块''')
七、Allure2报告中添加用例优先级
7.1 背景
-
应用场景:
- 用例执行时,希望按照严重级别执行测试用例。
-
解决:
- 可以为每个用例添加一个等级的装饰器。
-
用法:
@allure.severity
7.2 定义
- Allure对严重级别的定义分为5个级别:
- Blocker:中断缺陷(客户端程序无响应,无法执行下一步操作);
- Critical:临界缺陷(功能点缺失);
- Normal:普通缺陷(数值计算错误);
- Minor:次要缺陷(界面错误与UI需求不符);
- Trivial:轻微缺陷(必输项无提示,或者提示不规范)。
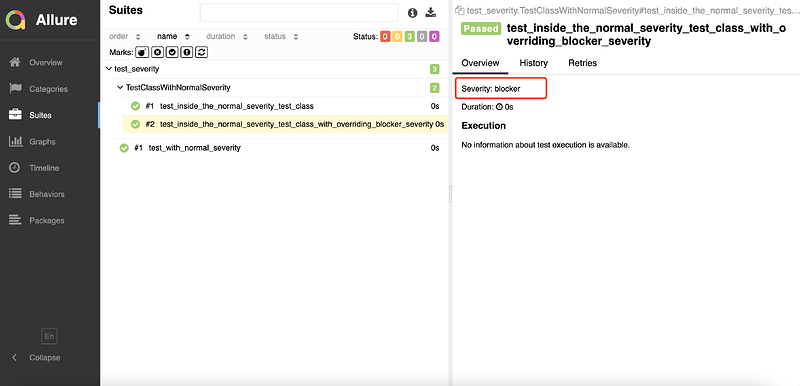
7.3 方法
- 使用装饰器添加用例方法/类的级别。
- 类上添加的级别,对类中没有添加级别的方法生效。
- 运行时添加命令行参数
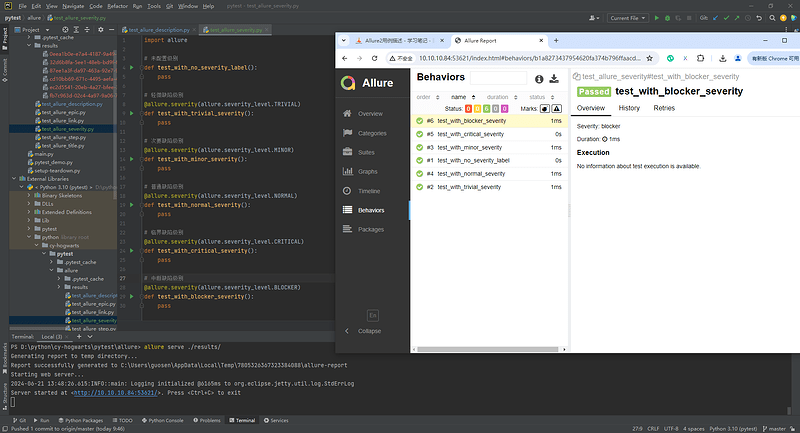
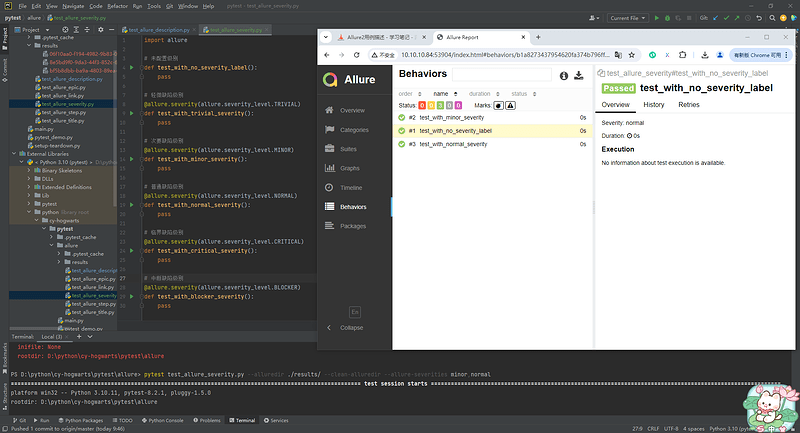
--allure-severities: pytest --alluredir ./results --clean-alluredir --allure-severities normal,blocker
import allure
def test_with_no_severity_label():
pass
@allure.severity(allure.severity_level.TRIVIAL)
def test_with_trivial_severity():
pass
@allure.severity(allure.severity_level.NORMAL)
def test_with_normal_severity():
pass
@allure.severity(allure.severity_level.NORMAL)
class TestClassWithNormalSeverity(object):
def test_inside_the_normal(self):
pass
@allure.severity(allure.severity_level.CRITICAL)
def test_critical_severity(self):
pass
@allure.severity(allure.severity_level.BLOCKER)
def test_blocker_severity(self):
pass
八、Allure2报告中添加用例支持tags标签
8.1 背景
- 应用场景:
- Allure报告支持的一些常见Pytest特性,包括xfail、skipif、fixture等。
- 测试结果会展示特定的标识在用例详情页面。
8.2 方法
- 使用装饰器:
@pytest.xfail()@pytest.skipif()
import pytest
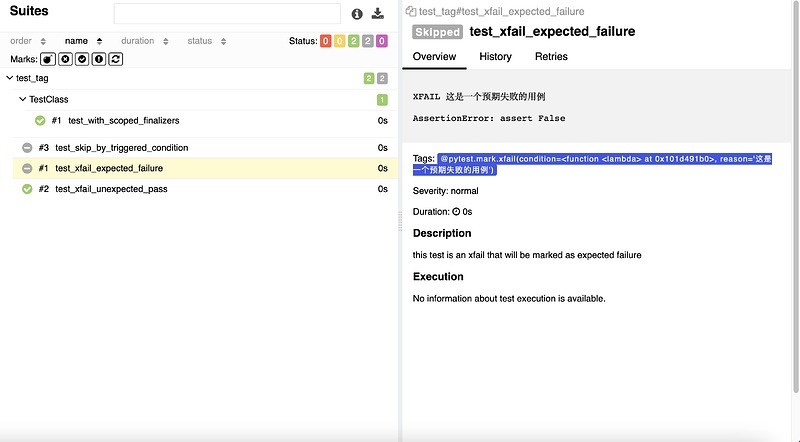
# 当用例通过时标注为 xfail
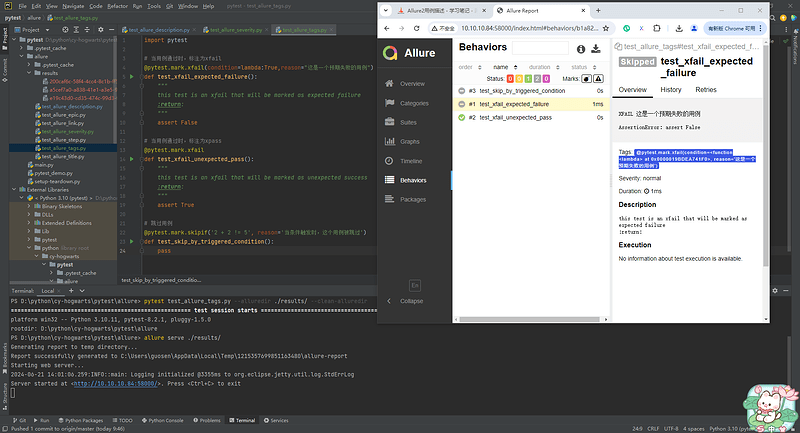
@pytest.mark.xfail(condition=lambda: True, reason='这是一个预期失败的用例')
def test_xfail_expected_failure():
"""this test is an xfail that will be marked as expected failure"""
assert False
# 当用例通过时标注为 xpass
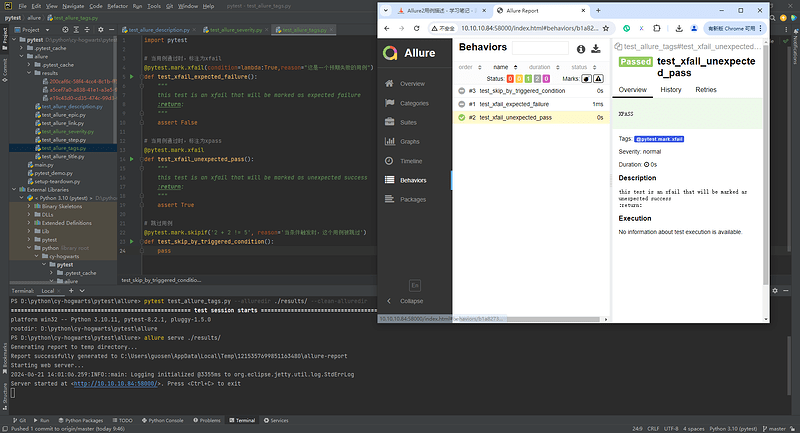
@pytest.mark.xfail
def test_xfail_unexpected_pass():
"""this test is an xfail that will be marked as unexpected success"""
assert True
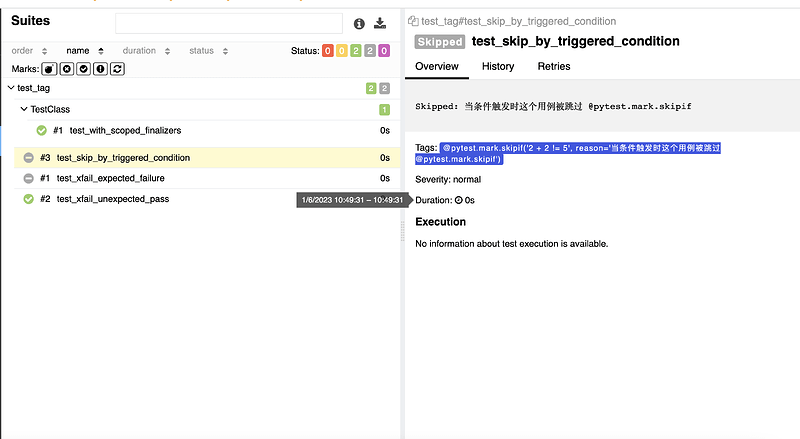
# 跳过用例
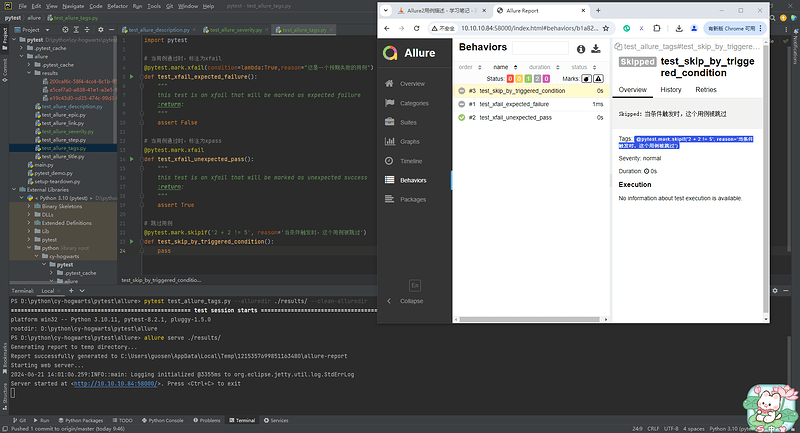
@pytest.mark.skipif('2 + 2 != 5', reason='当条件触发时这个用例被跳过 @pytest.mark.skipif')
def test_skip_by_triggered_condition():
pass
8.3 Allure2添加用例标签-fixture
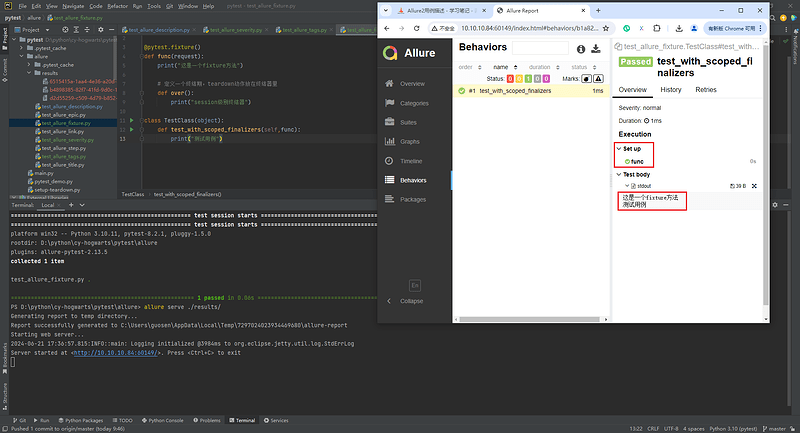
- 应用场景:
- fixture和finalizer是分别在测试开始之前和测试结束之后,由Pytest调用的使用程序函数。
- Allure跟踪每个fixture的调用,并详细显示调用了哪些方法以及哪些参数,从而保持了调用的正确顺序。
import pytest
@pytest.fixture()
def func(request):
print("这是一个fixture方法")
# 定义一个终结器,teardown动作放在终结器中
def over():
print("session级别终结器")
request.addfinalizer(over)
class TestClass(object):
def test_with_scoped_finalizers(self,func):
print("测试用例")
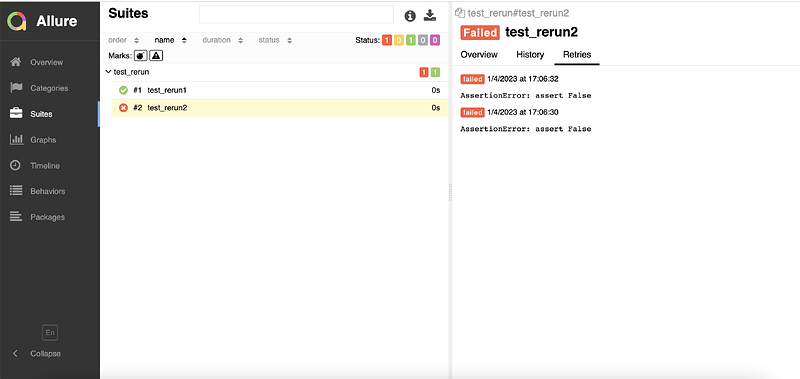
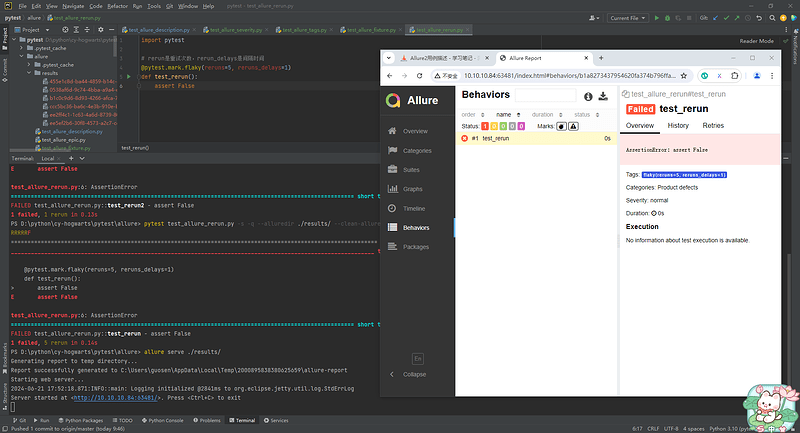
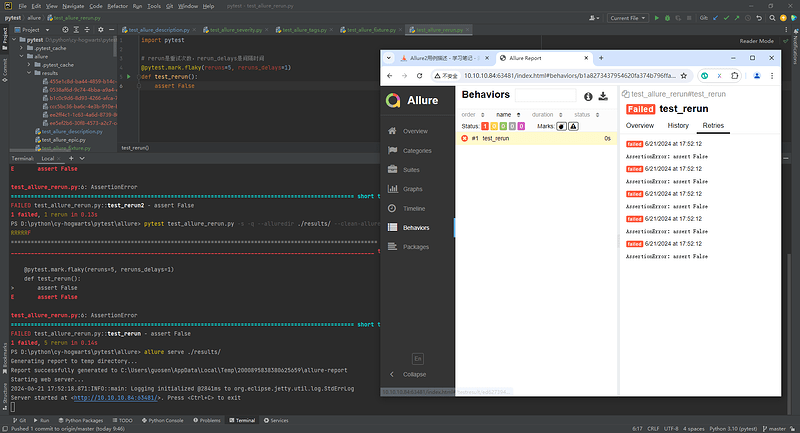
九、Allure2报告中支持记录失败重试功能
9.1 背景
- 应用场景:
- Allure可以收集用例运行期间,重试的用例的结果,以及这段时间重试的历史记录。
9.2 方法
- 重试功能可以使用Pytest相关的插件,例如
pytest-rerunfailures; - 重试的结果信息,会展示在详情页面的
Retries选项卡中。
import pytest
@pytest.mark.flaky(reruns=2, reruns_delays=2)
def test_rerun2():
assert False