pytest插件开发(常用的插件、pytest执行测试用例顺序控制、分布式执行测试用例、hook体系)
-
pytest插件分类
1、外部插件:pip install 安装的插件
2、本地插件:pytest 自动模块发现机制自动加载(conftest.py存放的,例如:fixture存放到conftest.py)
3、内置插件:代码内部的_pytest目录下加载,hook函数 -
pytest常用的插件
1、pip install pytest-ordering #控制用例的执行顺序(重点)
2、pip install pytest-xdist #分布式并发执行测试用例(重点)
3、pip install pytest-dependency #控制用例的依赖关系(了解)
4、pip install pytest-rerunfailures #失败重跑(了解)
5、pip install pytest-assume #多重校验(了解)
6、pip install pytest-random-order #用例随机执行(了解)
7、pip install pytest-html #测试报告(了解) -
pytest执行顺序控制
适用场景(步骤多的测试用例,排错步骤):
1、对于集成测试,经常会有上下文依赖关系的测试用例。例如10个步骤,拆成10条case,这时候使用pytest执行顺序控制,就能知道到底是执行到哪步开始报错。
2、用例默认的执行顺序为:自上而下执行
解决:
1、可以通过setup,teardown和fixture来解决。也可以使用对应的插件。
2、安装:pip install pytest-ordering
4、注意:多个插件装饰器(>2)的时候,有可能会发生冲突
5、非特殊情况不建议使用pytest-ordering控制测试用例执行顺序 -
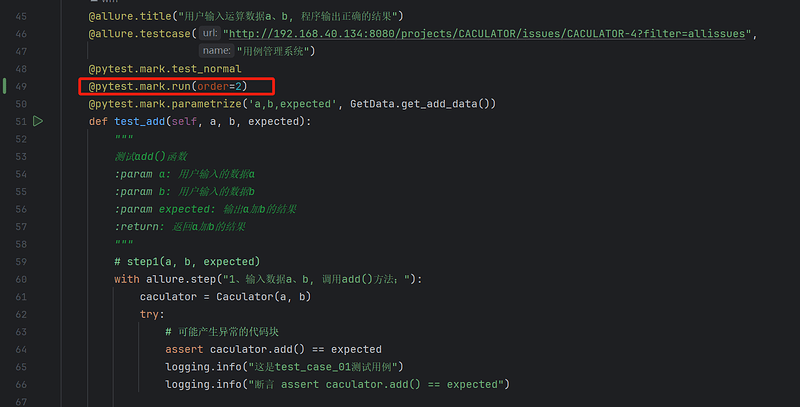
pytest-ordering用法:
@pytest.mark.run(order=2)
(git源码: pytest-ordering/pytest_ordering/init.py at develop · ftobia/pytest-ordering (github.com)
- pytest测试用例并行运行与分布式
场景 1:
测试用例 1000 条,一个用例执行 1 分钟,一个测试人员执行需要 1000 分钟。
通常我们会用人力成本换取时间成本,加几个人一起执行,时间就会 缩短。
如果 10 人一起执行只需要 100 分钟,这就是一种分布式场景。
场景 2:
假设有个报名系统,对报名总数统计,数据同时进行修改操作的时候有可能出现问题,
需要模拟这个场景,需要多用户并发请求数据。
解决:
使用分布式并发执行测试用例。分布式插件:pytest-xdist
安装及运行: pip install pytest-xdist
1、使用分布式并发执行测试用例,分布式插件:pytest-xdist
2、安装及运行:pip install pytest-xdist
3、注意:用例多的时候效果明显,多进程并发执行,同时支持allure
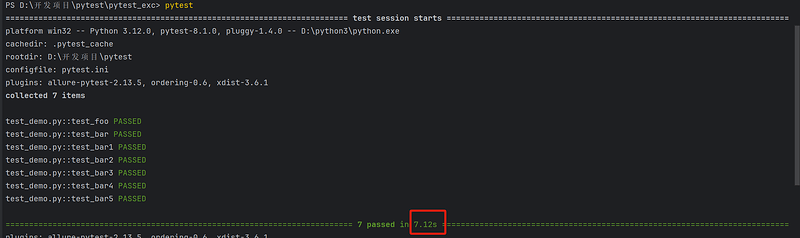
使用普通pytest命令的运行结果
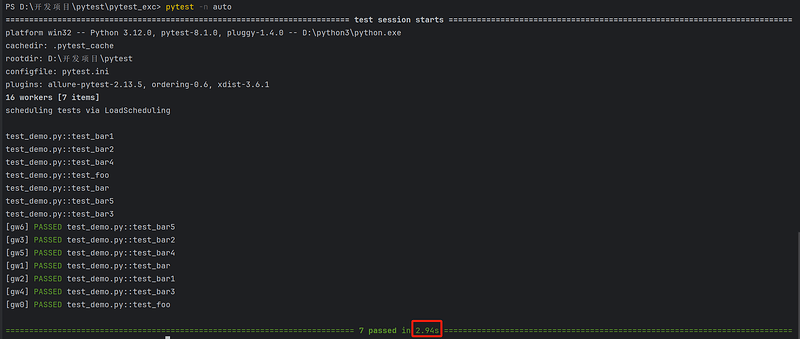
使用分布式命令pytest -n auto 执行命令的运行结果
-
分布式执行测试用例原则
1、用例之间是独立的,不能有依赖关系
2、用例执行没有顺序,随机顺序都能正常执行
3、每个用例都能重复运行,运行结果不会影响其他用例 -
pytest内置插件hook体系
pytest hook 介绍:
1、是个函数,在系统消息触发时被系统调用
2、自动触发机制
3、Hook函数的名称是确定的
4、pytest有非常多的钩子函数
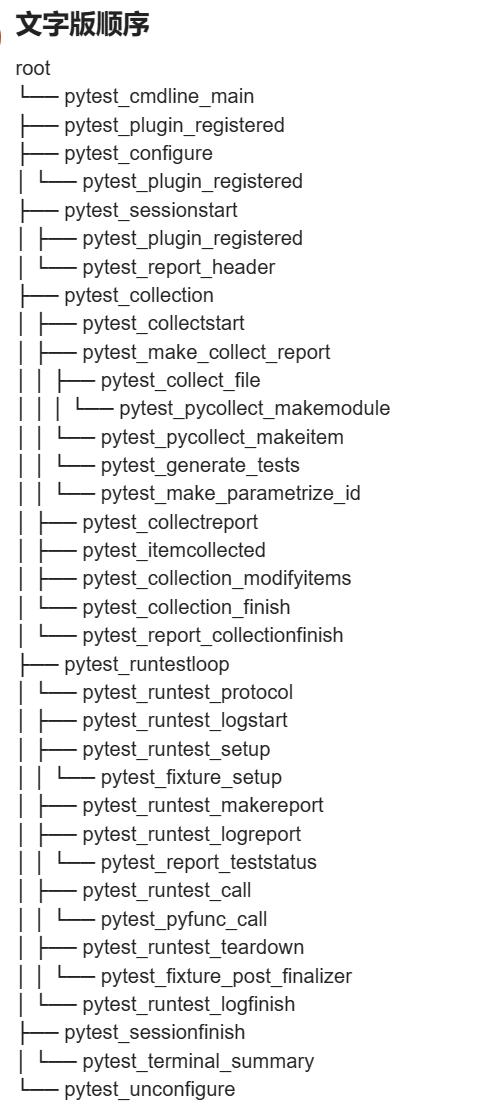
5、使用时直接编写函数体pytest hook 执行顺序:
site-package/_pytest/hookspec.py
pytest_addoption : 添加命令行参数,运时会先读取命令行参数
pytest_collection_modifyitems : 收集测试用例,收集之后(改编码,改执行顺序)
pytest_collection_finish:收集之后的操作
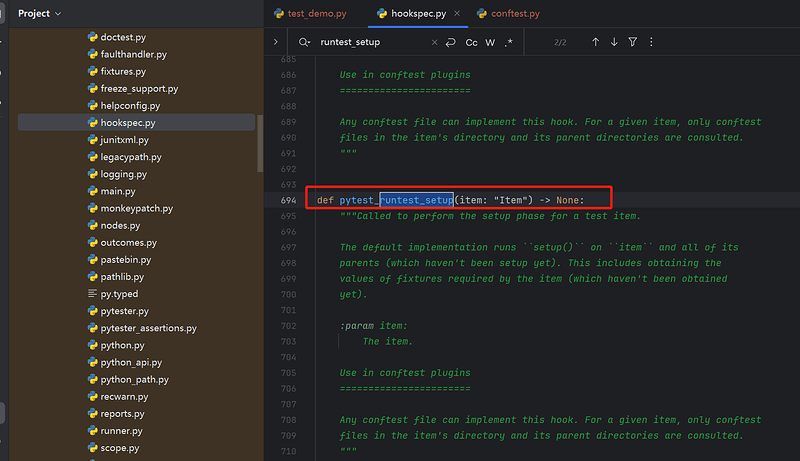
pytest_runtest_setup:在调用 pytest_runtest_call 之前调用
pytest_runtest_call:调用执行测试的用例
pytest_runtest_makereport:运行测试用例,返回setup,call,teardown的执行结果
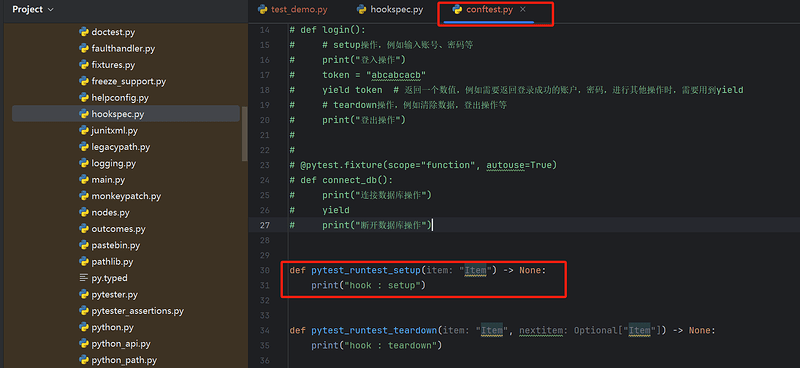
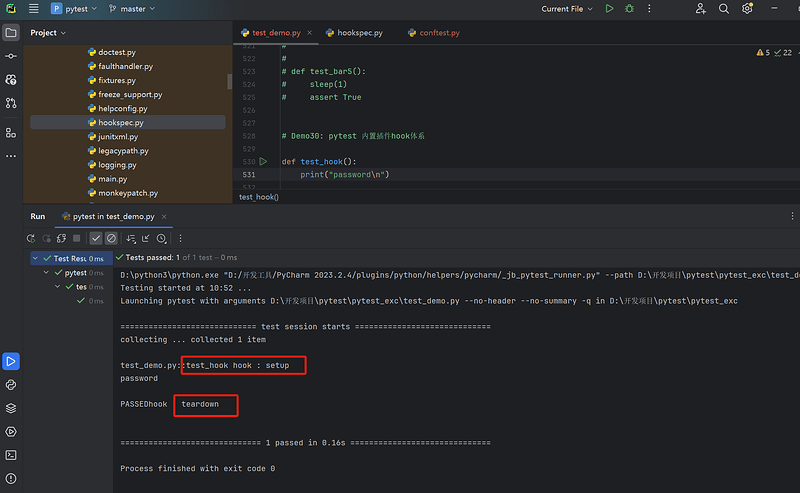
- 简单的例子
1、首先在 /ExternalLibraries/site-packages/_pytest/ 路径下编辑hookspec.py
2、将需要重写的hook函数复制到conftest.py文件中,并在conftest.py文件中重写hook函数
3、程序会自动执行重写后的hook函数
def pytest_runtest_setup(item):
# 执行测试用例前执行的setup方法
print("setting up", item)
def pytest_runtest_call(item):
# 调用执行测试的用例
print("pytest_runtest_call")
def pytest_runtest_teardown(item):
# 执行测试用例后执行的teardown
print("pytest runtest teardown",item)
- 总结
1、hook 函数名字固定
2、hook 函数会被自动执行
3、执行是有先后顺序的
4、pytest 定义了很多 hook 函数,可以在不同阶段实现不同的功能