一,Junit5测试套件@Suite
-
JUnit5通过@Suite注解使用套件 - 不需要再声明
@RunWith(JUnitPlatform.class) - 如果项目是从
Junit4进行迁移,仍然需要@RunWith(JUnitPlatform.class)
1.1 对应依赖导入
<dependency>
<groupId>org.junit.platform</groupId>
<artifactId>junit-platform-suite</artifactId>
<version>1.8.2</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
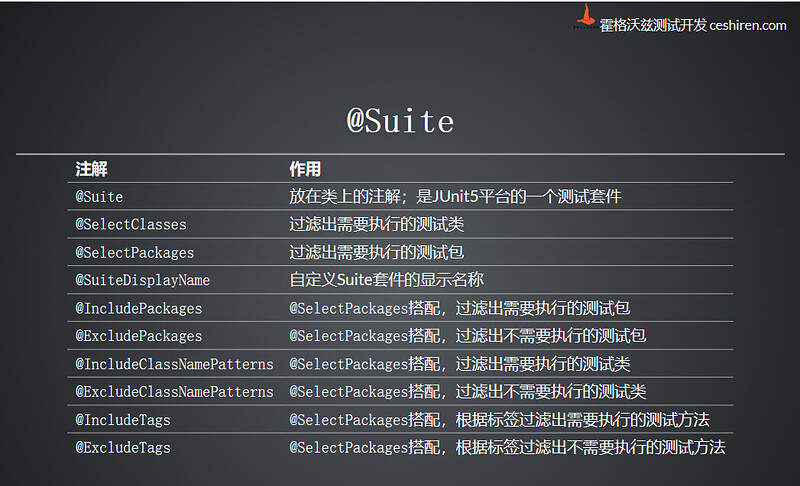
1.2 Suite注解说明
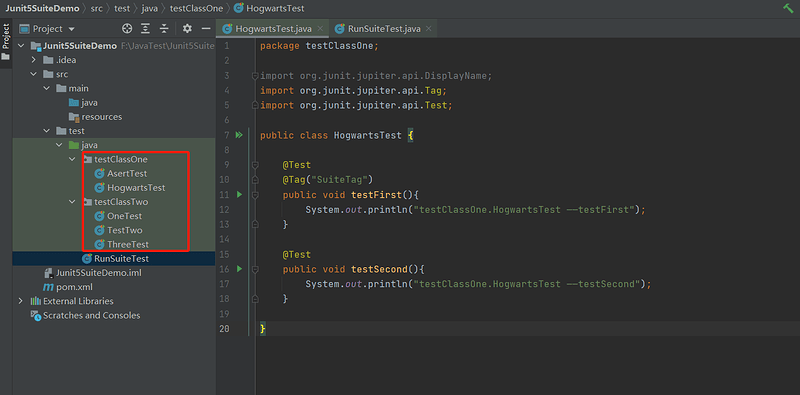
1.3 代码示例
对应的测试包和测试类:
测试套件:
import org.junit.platform.suite.api.*;
//Suite基本注解
@Suite
@SuiteDisplayName("Test Suite测试套件") //自定义Suite套件的显示名称
//@SelectClasses(AsertTest.class) //选择需要执行的单个测试类
//@SelectClasses({OneTest.class, TwoTest.class}) //可以选择多个测试类,参数类型为集合{}
//@SelectPackages("testClassOne") //选择需要执行的测试包,参数类型为String
@SelectPackages({"testClassOne","testClassTwo"}) //可以选择多个测试包,参数类型为集合{}
//@IncludePackages("testClassOne") //必须和SelectPackages结合使用,并且满足SelectPackages条件的包名才能执行
//@ExcludePackages("testClassOne") //满足SelectPackages条件的包名,然后过滤ExcludePackages中的包名
//@IncludeClassNamePatterns({"testClassOne.*","testClassTwo.*Test"}) //满足SelectPackages条件的包名,对应正则表达式匹配的class测试类执行
//@ExcludeClassNamePatterns("testClassTwo.*Test") //满足SelectPackages条件的包名,对应正则表达式匹配的class测试类不被执行
//@IncludeTags({"SuiteTag","SuiteTag1"}) //满足SelectPackages条件的包名,包含对应标签的测试类被执行
@ExcludeTags("SuiteTag") //满足SelectPackages条件的包名,包含对应标签的测试类不被执行
public class RunSuiteTest {
}
二,多断言处理
2.1 集中断言使用方式
- 拆开多个测试方法,每个测试方法进行一个断言。(会造成大量重复代码,此方案被否)
- 使用assertAll软断言,即使一个断言失败,仍会进行进行余下的断言,然后统一输出所有断言结果。
- 声明
ArrayList<Executable>进行集中断言
2.2 代码示例
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.function.Executable;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertAll;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertEquals;
public class AssertListTest {
@Test
void addTest(){
assertAll(
() ->assertEquals(9,2+7),
() ->assertEquals(3,2+1));
}
@Test
void listTest(){
//声明ArrayList<Executable>进行断言
ArrayList<Executable> arr = new ArrayList<>();
for(int i=0; i<5; i++){
int res = 1 + i;
arr.add(
//将中间结果保存到list中,以备后面统一断言
() -> assertEquals(3, res));
}
assertAll(arr.stream());
}
}
三,高级断言hamcrest
3.1 导入依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.hamcrest</groupId>
<artifactId>hamcrest</artifactId>
<version>2.2</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
3.2 常用断言匹配
package hamcrestDemo;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
import static org.hamcrest.MatcherAssert.assertThat;
import static org.hamcrest.Matchers.*;
import static org.hamcrest.Matchers.hasItems;
public class HamcrestDemoTest {
// is(T):将一个对象作为参数来检查相等性
// is(Matcher<T>): 使用另一个匹配器,使相等性语句更具表现力
@Test
void IsForMatch(){
String str = "hamcrest core Is match";
assertThat(str,is("hamcrest core Is match"));
assertThat(str,is(equalTo("hamcrest core Is match")));
}
//equalTo(T): 将一个对象作为参数并检查其与另一个对象的相等性
//经常与 is(Matcher<T>) 一起使用
@Test
void EuqalToMatch(){
String str = "equalTo match";
List<String> list = Arrays.asList("equalTo","match");
Object obj = 100;
assertThat(str,equalTo("equalTo match"));
assertThat(str,is(equalTo(list)));
assertThat(obj,equalToObject(100));
assertThat(str,equalToObject("equalTo match"));
}
//not(T): 接受一个对象作为参数,检查给定对象的不相等性
//not(Matcher<T>): 接受另一个匹配器
@Test
void notForMatch(){
String str = "hamcrest core not match";
assertThat(str,not("hamcrest other match"));
assertThat(str,not(equalToObject("hamcrest other match")));
assertThat(str,is(not(instanceOf(Integer.class))));
}
//hasItem(T)/hasItem(Matcher<? extends T>) : 检查参数是否与给定对象或匹配器匹配,是否包含
//使用hasItems也可以对多个项目进行断言,其中一个包含,则为true
@Test
void HasItemMatch(){
List<String> list = Arrays.asList("java", "hamcrest", "JUnit5");
assertThat(list,hasItem("java"));
assertThat(list, hasItem(isA(String.class)));
assertThat(list, hasItems("java","JUnit5"));
assertThat(list, hasItems(isA(String.class),endsWith("est")));
}
//allOf(Matcher<? extends T>…): 断言实际对象是否与所有指定条件匹配
@Test
void AllOfForMatch(){
String testString = "Achilles is powerful";
assertThat(testString, allOf(
startsWith("Achi"), endsWith("ul"), containsString("Achilles")));
}
//anyOf(Matcher<? extends T>…): 检查的对象匹配任何指定的条件,则匹配
@Test
void AnyOfForMatch(){
String testString2 = "Hector killed Achilles";
assertThat(testString2, anyOf(startsWith("Heca"), containsString("killed")));
}
//both(Matcher<? extends T>):和 and 配合使用,两个指定条件都匹配检查对象时匹配
@Test
void BothForMatch(){
String str = "daenerys targaryen";
assertThat(str,both(startsWith("dae")).and(endsWith("yen")));
}
//either(Matcher<? extends T>):和 or 配合使用,任一指定条件与检查对象匹配时匹配
@Test
void UsingBothForMatch(){
String testString = "daenerys targaryen";
assertThat(testString, either(startsWith("tar")).or(containsString("targaryen")));
}
}
四,yaml数据驱动
-
使用Jackson读取yaml文件数据
-
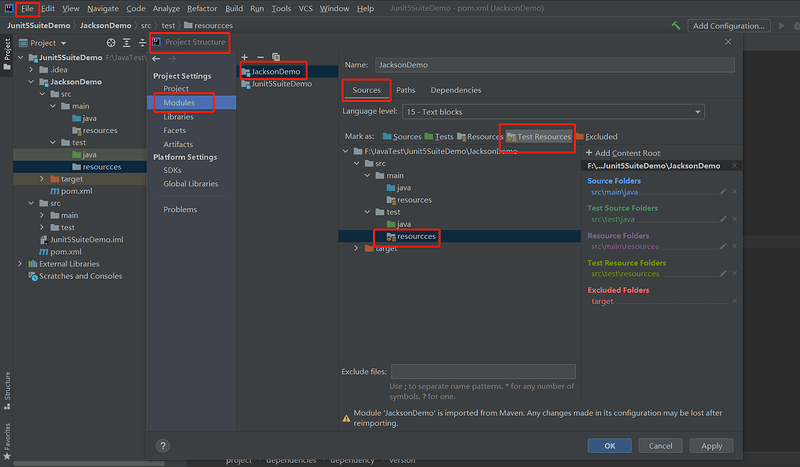
yaml文件存放目录:src/test/resources目录下面,
resources目录配置:点击file - 选择Project Structure - 选择Modules - 右边选择你需要修改的模块名称,在sources栏下面找到新建的resources目录,然后点击Test Resources,点击保存,目录就设置好了。
4.1 导入maven依赖
<properties>
<maven.compiler.source>15</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>15</maven.compiler.target>
<jackson.version>2.13.1</jackson.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<!--yaml文件解析-->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.core</groupId>
<artifactId>jackson-databind</artifactId>
<version>${jackson.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.dataformat</groupId>
<artifactId>jackson-dataformat-yaml</artifactId>
<version>${jackson.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.datatype</groupId>
<artifactId>jackson-datatype-jsr310</artifactId>
<version>${jackson.version}</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
4.2 直接解析list文件
-
在Resources目录下面新建一个yaml文件 - orderlist.yaml,里面存放的数据类型为list。
-
解析list文件,见下记代码
import com.fasterxml.jackson.core.type.TypeReference;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.dataformat.yaml.YAMLFactory;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.math.BigDecimal;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import static org.hamcrest.MatcherAssert.assertThat;
import static org.hamcrest.Matchers.*;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertAll;
public class yamlTest {
@Test
public void orderlistTest() throws IOException {
//创建ObjectMapper对象
ObjectMapper mapper = new ObjectMapper(new YAMLFactory());
//获取文件数据类型信息
TypeReference<List<HashMap<String,Object>>> typeReference = new TypeReference<List<HashMap<String, Object>>>() {
};
//读取文件内容
List<HashMap<String,Object>> hashMaps = mapper.readValue(new File("src/test/resources/orderlist.yaml"),
typeReference);
// System.out.println(hashMaps);
hashMaps.forEach(hashMap ->{
assertAll(
() ->assertThat(hashMap.get("item").toString(), startsWith("No")),
() -> assertThat(Integer.parseInt(hashMap.get("quantity").toString()),
is(greaterThan(9))),
() -> assertThat(new BigDecimal(hashMap.get("unitPrice").toString()),
is(closeTo(new BigDecimal(1.0),new BigDecimal(4.00))))
);
});
}
}
4.3 新建一个实体类,来解析文件数据
*使用alt+insert 快捷键批量城市getter和setter方法,以及构造方法(点击Constructors)
- 新建一个实体类,成员变量与yaml的key不一致
(成员变量与yaml的key不一致的情况下,打印的数据key会是实体类重新定义的key)
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonProperty;
import java.math.BigDecimal;
import java.time.LocalDate;
//定义一个实体类,成员变量与yaml的key不一致
@Data
public class OrderList {
@JsonProperty("item")
private String items;
@JsonProperty("quantity")
private int number;
@JsonProperty("unitPrice")
private BigDecimal price;
@JsonProperty("orderDate")
private LocalDate data;
public OrderList() {
}
public OrderList(String items, int number, BigDecimal price, LocalDate data) {
this.items = items;
this.number = number;
this.price = price;
this.data = data;
}
public String getItems() {
return items;
}
public void setItems(String items) {
this.items = items;
}
public int getNumber() {
return number;
}
public void setNumber(int number) {
this.number = number;
}
public BigDecimal getPrice() {
return price;
}
public void setPrice(BigDecimal price) {
this.price = price;
}
public LocalDate getData() {
return data;
}
public void setData(LocalDate data) {
this.data = data;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "OrderList{" +
"items='" + items + '\'' +
", number=" + number +
", price=" + price +
", data=" + data +
'}';
}
}
- 新建一个实体类,成员变量与yaml的key一致(更推荐使用这种实体类的形式)
import lombok.Data;
import java.math.BigDecimal;
import java.time.LocalDate;
@Data
public class OrderLine {
private String item;
private int quantity;
private BigDecimal unitPrice;
private LocalDate orderDate;
public OrderLine() {
}
public OrderLine(String item, int quantity, BigDecimal unitPrice, LocalDate orderDate) {
this.item = item;
this.quantity = quantity;
this.unitPrice = unitPrice;
this.orderDate = orderDate;
}
public String getItem() {
return item;
}
public void setItem(String item) {
this.item = item;
}
public int getQuantity() {
return quantity;
}
public void setQuantity(int quantity) {
this.quantity = quantity;
}
public BigDecimal getUnitPrice() {
return unitPrice;
}
public void setUnitPrice(BigDecimal unitPrice) {
this.unitPrice = unitPrice;
}
public LocalDate getOrderDate() {
return orderDate;
}
public void setOrderDate(LocalDate orderDate) {
this.orderDate = orderDate;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "OrderLine{" +
"item='" + item + '\'' +
", quantity=" + quantity +
", unitPrice=" + unitPrice +
", orderDate=" + orderDate +
'}';
}
}
- 通过实体类解析yaml数据
@Test
void orderListTest() throws IOException {
ObjectMapper mapper = new ObjectMapper(new YAMLFactory());
//功能上等价的便捷方法: mapper.registerModules(mapper.findModules());
//我们需要使用 findAndRegisterModules方法,以便 Jackson正确处理我们的日期,Jackson也可以自动搜索所有模块,不需要我们手动注册
mapper.findAndRegisterModules();
//获取数据类型为实体类名OrderList
TypeReference<List<OrderList>> typeReference = new TypeReference<List<OrderList>>() {
};
List<OrderList> mapList = mapper.readValue(new File("src/test/resources/orderlist.yaml"),typeReference);
System.out.println(mapList);
mapList.forEach(orderList ->{
assertAll(
() ->assertThat(orderList.getItem(),startsWith("No.")),
() ->assertThat(orderList.getQuatity(),is(greaterThan(9))),
() ->assertThat(orderList.getUnitPrice(),is(closeTo(new BigDecimal(1.0),new BigDecimal(4.0))))
);
});
}
五,JUnit5结合数据驱动 - excel解析
- 推荐使用Apache POI解析Excel
1,导入依赖
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.apache.poi/poi -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.poi</groupId>
<artifactId>poi</artifactId>
<version>5.2.2</version>
</dependency>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.apache.poi/poi-ooxml -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.poi</groupId>
<artifactId>poi-ooxml</artifactId>
<version>5.2.2</version>
</dependency>
2,poi解析
- 获取文件名后缀
- 查看文件是否存在
- 获取工作薄对象
Workbook- 如果是
xls结尾用HSSF - 如果是
xlsx结尾用XSSF - 使用输入流的形式打开文件获取工作薄对象
- 直接使用file打开文件获取工作薄对象
- 如果是
- 读取第一个
sheet - 获取行
- 读取每一行的单元格内容
- 最后关闭流
import org.apache.poi.hssf.usermodel.HSSFWorkbook;
import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.*;
import org.apache.poi.xssf.usermodel.XSSFWorkbook;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import static org.hamcrest.MatcherAssert.assertThat;
import static org.hamcrest.Matchers.anyOf;
import static org.hamcrest.Matchers.endsWithIgnoringCase;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertTrue;
public class PoiDemoTest {
@Test
void poiTest(){
try {
//1,获取文件名后缀
String pathname = "src/test/resources/order.xls";
String excelType = pathname.substring(pathname.lastIndexOf(".") + 1, pathname.length());
//判断文件后缀是否正确
assertThat("文件不是excel文件", excelType, anyOf(endsWithIgnoringCase("xls"), endsWithIgnoringCase("xlsx")));
//2,判断文件是否存在
File file = new File(pathname);
assertTrue(file.exists(),"文件excel不存在!");
//3,获取文件Workbook
FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream(file);
Workbook workbook = null;
//xls结尾的文件用HSSF,xlsx结尾的用XSSF
if (excelType.equalsIgnoreCase("xls")) {
workbook = new HSSFWorkbook(fileInputStream);
} else if(excelType.equalsIgnoreCase("xlsx")){
workbook = new XSSFWorkbook(fileInputStream);
}
//获取当前工作簿有多少个sheet表格
int numberOfSheets = workbook.getNumberOfSheets();
//4,读取第一个sheet表格,对应sheet是从0开始
Sheet sheet = workbook.getSheetAt(0);
//获取当前sheet有多少行
int numberOfRows = sheet.getPhysicalNumberOfRows();
//一个sheet对应的数据结构对象map<行号,行的内容>
Map<Integer, List<Object>> data = new HashMap<>();
//5,读取每一行的数据
//行号
int i=0;
for(Row row :sheet){
//把每行的数据添加到列表里
data.put(i,new ArrayList<>());
// System.out.println(row); //打印读取到的是行的对象,而非对象内容
//每一行是row,是一个list,获取一行有多少个单元格
int numberOfCells = row.getPhysicalNumberOfCells();
// System.out.println("每行有多少个单元格:"+ numberOfCells );
//每行的每个单元格是cell
for(Cell c:row){
// System.out.println(c); //打印每一行每一个单元格的数据内容
List<Object> list = data.get(i);
//单元格类型枚举值为STRING时,将使用Cell接口的getRichStringCellValue()方法读取内容:
//文本格式的内容读取
switch(c.getCellType()){
case STRING:
// String string = c.getRichStringCellValue().getString();
// list.add(string);
list.add(c.getRichStringCellValue().getString());
break;
//NUMERIC - 数字,日期
case NUMERIC:
if(DateUtil.isCellDateFormatted(c)) {
//日期型以年-月-日格式存储
SimpleDateFormat fmt = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd");
list.add(fmt.format(c.getDateCellValue()));
}else{
list.add(c.getNumericCellValue());
}
break;
case BOOLEAN:
list.add(c.getBooleanCellValue());
break;
case FORMULA:
list.add(c.getCellFormula());
break;
default:
list.add(" ");
}
}
i++;
}
System.out.println("data : "+ data);
//关闭流
workbook.close();
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
六,JUnit5结合数据驱动 - csv解析
1,pom依赖导入
<properties>
<maven.compiler.source>11</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>11</maven.compiler.target>
<jackson.version>2.13.1</jackson.version>
</properties>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.dataformat</groupId>
<artifactId>jackson-dataformat-csv</artifactId>
<version>${jackson.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.datatype</groupId>
<artifactId>jackson-datatype-jsr310</artifactId>
<version>${jackson.version}</version>
</dependency>
2,解析csv文件
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.MappingIterator;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.dataformat.csv.CsvMapper;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.dataformat.csv.CsvSchema;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Order;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
public class CsvDemoTest {
//带header的csv文件解析
@Test
void csvReadHeader() throws IOException {
//带着header读取(会把item等列名一并读取出来)
CsvSchema columns = CsvSchema.emptySchema().withHeader();
CsvMapper csvMapper = new CsvMapper();
//功能上等价的便捷方法: mapper.registerModules(mapper.findModules());
//我们需要使用 findAndRegisterModules方法,以便 Jackson正确处理我们的日期,不加的话解析日期会报错
csvMapper.findAndRegisterModules();
//成员变量与header名一致的情况下读取
MappingIterator<OrderLine> orderLines = csvMapper.readerFor(OrderLine.class).
with(columns).readValues(new File("src/test/resources/csv/orderLine.csv"));
System.out.println(orderLines.readAll());
//打印结果:[OrderLine{item='No. 9 Sprockets', quantity=12, unitPrice=1.23, orderDate=2019-04-17}, OrderLine{item='No. Widget (10mm)', quantity=10, unitPrice=3.45, orderDate=2022-01-16}]
//成员变量与header名不一致的情况下读取
MappingIterator<OrderList> orderList = csvMapper.readerFor(OrderList.class).
with(columns).readValues(new File("src/test/resources/csv/orderList.csv"));
System.out.println(orderList.readAll());
//打印结果:[OrderList{items='No. 9 Sprockets', number=12, price=1.23, data=2019-04-17}, OrderList{items='No. Widget (10mm)', number=10, price=3.45, data=2022-01-16}]
}
//跳过header,readerForMapOf直接声明类型解析
@Test
void csvReadWithoutHeader() throws IOException {
//第一行header不解析,自行加上列名
CsvSchema schema = CsvSchema.builder().setSkipFirstDataRow(true)
.addColumn("item",CsvSchema.ColumnType.STRING)
.addColumn("quantity",CsvSchema.ColumnType.NUMBER)
.addColumn("unitPrice",CsvSchema.ColumnType.NUMBER)
.addColumn("orderDate",CsvSchema.ColumnType.STRING)
.build();
CsvMapper csvMapper = new CsvMapper();
MappingIterator<Object> orderLineMappingIterator = csvMapper.readerForMapOf(String.class)
.with(schema)
.readValues(new File("src/test/resources/csv/orderLine.csv"));
System.out.println(orderLineMappingIterator.readAll());
//打印数据结果:[{item=No. 9 Sprockets, quantity=12, unitPrice=1.23, orderDate=2019-04-17}, {item=No. Widget (10mm), quantity=10, unitPrice=3.45, orderDate=2022-01-16}]
}
//没有header的csv文件解析
@Test
void csvReadNoHeader() throws IOException {
CsvSchema schema = new CsvSchema.Builder()
.addColumn("item")
.addColumn("quantity")
.addColumn("unitPrice")
.addColumn("orderDate")
.build();
CsvMapper csvMapper = new CsvMapper();
csvMapper.findAndRegisterModules();
//成员变量与header名一致的情况下读取
MappingIterator<Object> mappingIterator = csvMapper.readerFor(OrderLine.class)
.with(schema)
.readValues(new File("src/test/resources/csv/data.csv"));
System.out.println(mappingIterator.readAll());
//打印结果:[OrderLine{item='No. 9 Sprockets', quantity=12, unitPrice=1.23, orderDate=2019-04-17}, OrderLine{item='No. Widget (10mm)', quantity=10, unitPrice=13.45, orderDate=2022-01-16}]
//成员变量与header名一致的情况下读取
MappingIterator<Object> mappingIterator1 = csvMapper.readerFor(OrderList.class)
.with(schema)
.readValues(new File("src/test/resources/csv/data.csv"));
System.out.println(mappingIterator1.readAll());
//打印结果:[OrderList{items='No. 9 Sprockets', number=12, price=1.23, data=2019-04-17}, OrderList{items='No. Widget (10mm)', number=10, price=13.45, data=2022-01-16}]
//readerForMapOf 直接声明类型解析
MappingIterator<Object> mappingIterator2 = csvMapper.readerForMapOf(String.class)
.with(schema)
.readValues(new File("src/test/resources/csv/data.csv"));
System.out.println(mappingIterator2.readAll());
//打印结果:[{item=No. 9 Sprockets, quantity=12, unitPrice=1.23, orderDate=2019-04-17}, {item=No. Widget (10mm), quantity=10, unitPrice=13.45, orderDate=2022-01-16}]
}
}
七,JUnit5结合数据驱动 - json文件解析
1,pom文件依赖导入
<dependency>
<groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.core</groupId>
<artifactId>jackson-databind</artifactId>
<version>${jackson.version}</version>
</dependency>
2,示例代码
import com.fasterxml.jackson.core.JsonFactory;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.core.JsonProcessingException;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.core.type.TypeReference;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;
import org.apache.poi.ss.formula.functions.T;
import org.aspectj.weaver.ast.Or;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
public class JsonDemoTest {
//1,直接声明类型,解析list类型的json文件
@Test
void orderMap() throws IOException {
ObjectMapper mapper = new ObjectMapper(new JsonFactory());
TypeReference<List<HashMap<String,Object>>> typeReference = new TypeReference<List<HashMap<String, Object>>>() { };
List<HashMap<String,Object>> hashMapList = mapper.readValue(new File("src/test/resources/order.json"),typeReference);
System.out.println(hashMapList.toString());
//打印结果:[{unitPrice=1.23, item=No. 9 Sprockets, quantity=12, orderDate=2019-04-17}, {unitPrice=3.45, item=No. Widget (10mm), quantity=10, orderDate=2022-01-16}]
}
//2,声明实体类,解析list类型的json文件
@Test
void OrderLineData() throws IOException {
ObjectMapper mapper = new ObjectMapper(new JsonFactory());
mapper.findAndRegisterModules();
TypeReference<List<OrderLine>> typeReference = new TypeReference<List<OrderLine>>() { };
List<OrderLine> orderLines = mapper.readValue(new File("src/test/resources/order.json"),typeReference);
System.out.println(orderLines);
//打印结果:[OrderLine{item='No. 9 Sprockets', quantity=12, unitPrice=1.23, orderDate=2019-04-17}, OrderLine{item='No. Widget (10mm)', quantity=10, unitPrice=3.45, orderDate=2022-01-16}]
}
// 3,解析一个HashMap的json文件数据
@Test
void listJson() throws IOException {
//直接声明类型
ObjectMapper mapper = new ObjectMapper(new JsonFactory());
TypeReference<HashMap<String,Object>> typeReference = new TypeReference<HashMap<String, Object>>() { };
HashMap<String,Object> objectHashMap = mapper.readValue(new File("src/test/resources/list.json"),typeReference);
System.out.println(objectHashMap);
//打印结果:{date=2019-04-17, orderNo=A001, orderLines=[{item=No. 9 Sprockets, quantity=12, unitPrice=1.23}, {item=No. Widget (10mm), quantity=40, unitPrice=3.45}], customerName=Customer, Joe}
//声明一个实体类Order,解析json文件
TypeReference<Order> typeReference1 = new TypeReference<Order>() { };
mapper.findAndRegisterModules();
Order order = mapper.readValue(new File("src/test/resources/list.json"),typeReference1);
System.out.println(order);
//打印结果:Order{orderNo='A001', date=2019-04-17, customerName='Customer, Joe', orderLines=[OrderLine{item='No. 9 Sprockets', quantity=12, unitPrice=1.23, orderDate=null}, OrderLine{item='No. Widget (10mm)', quantity=40, unitPrice=3.45, orderDate=null}]}
}
}
八,Junit5执行并行策略
1,用例准备(同一模块3个测试类)
import org.junit.jupiter.api.RepeatedTest;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.parallel.Execution;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.parallel.ExecutionMode;
public class ParallelOneTest {
@Test()
// @RepeatedTest()
@Execution(ExecutionMode.CONCURRENT)
void test1(){
String name = Thread.currentThread().getName(); //线程名
System.out.println(name + " => ParallelOneTest —— test1");
}
@Test
void test2(){
String name = Thread.currentThread().getName();
System.out.println(name + " => ParallelOneTest —— test2");
}
@Test
void test3(){
String name = Thread.currentThread().getName();
System.out.println(name + " => ParallelOneTest —— test3");
}
}
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
public class ParallelTwoTest {
@Test
void test01(){
String name = Thread.currentThread().getName();
System.out.println(name + " => ParallelTwoTest —— test01");
}
@Test
void tes02(){
String name = Thread.currentThread().getName();
System.out.println(name + " => ParallelTwoTest —— test02");
}
@Test
void test03(){
String name = Thread.currentThread().getName();
System.out.println(name + " => ParallelTwoTest —— test03");
}
}
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
public class ParallelThreeTest {
@Test
void test001(){
String name = Thread.currentThread().getName();
System.out.println(name + " => ParallelThreeTest —— test001");
}
@Test
void tes002(){
String name = Thread.currentThread().getName();
System.out.println(name + " => ParallelThreeTest —— test002");
}
@Test
void test003(){
String name = Thread.currentThread().getName();
System.out.println(name + " => ParallelThreeTest —— test003");
}
}
2,并行配置
-
全局并发配置:
junit.jupiter.execution.parallel.enabled的值设置为true -
局部并发配置:@RepeatedTest和@@Execution(ExecutionMode.CONCURRENT)
-
如果没有并发配置,默认就是主「
main」线程运行。 -
如果要开启并行,则需配置并行测试的
parallel参数。 -
注意:启用此属性只是并行执行测试所需的第一步。
- 如果启用,默认情况下测试类和方法仍将按顺序执行。
-
测试使用ForkJoin线程池
3,配置方式
(1)在JUnit5的配置文件「junit-platform.properties」进行配置 (最简单的方法)
- 在项目的
src/test/resources目录下创建JUnit5的配置文件:junit-platform.properties - 在配置文件加上配置:junit.jupiter.execution.parallel.enabled=true
(2)通过向 maven surefire 插件提供参数
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-surefire-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.0.0-M5</version>
<configuration>
<argLine>
-Djunit.jupiter.execution.parallel.enabled=true
</argLine>
</configuration>
</plugin>
(3)通过向 JVM 提供系统属性
mvn clean test -Djunit.jupiter.execution.parallel.enabled=true
4,并行执行模式
(1)执行模式可以使用以下两种模式:
- SAME_THREAD :强制在父级使用的同一线程中执行(单线程)。
- CONCURRENT :并发执行,除非资源锁强制在同一线程中执行。
- 默认情况下,所有的测试用例中的测试方法使用的是
SAME_THREAD执行模式。
(2)执行模式配置方法
- 使用属性配置,通过设置配置参数
junit.jupiter.execution.parallel.mode.default来更改默认值。在配置文件配置,全局生效。
#是否允许并行执行
junit.jupiter.execution.parallel.enabled=true
#支持方法级别多线程模式 - same_thread/concurrent
junit.jupiter.execution.parallel.mode.default = same_thread
#支持类级别多线程模式 - same_thread/concurrent
junit.jupiter.execution.parallel.mode.classes.default = concurrent
- 使用
@Execution注解单独更改对应的测试类及其子类或者测试方法的执行模式。- 配置文件的配置是全局生效
- 注解是针对具体测试类或测试方法
- 注解的优先级 高于 > 配置文件
@Test()
@RepeatedTest(6) //RepeatedTest表示重复测试执行的次数
@Execution(ExecutionMode.SAME_THREAD)
void test1(){
String name = Thread.currentThread().getName();
System.out.println(name + " => ParallelOneTest —— test1");
}
5,并行策略
-
JUnit提供了两种实现(动态和固定)和一个自定义选项。 -
junit.jupiter.execution.parallel.config.strategy的值设为并行策略配置参数中的一种即可。- 并发策略的配置参数有3种:
dynamic、fixed、custom - 前两种
dynamic和fixed是JUnit平台提供的 开箱即用 的实现。 -
custom策略是通过自定义的模式来配置并行的线程池数量。
- 并发策略的配置参数有3种:
- 如果没有进行策略的相关配置,并行化策略默认为
dynamic
(1)dynamic 动态策略
- 文件配置策略:junit.jupiter.execution.parallel.config.strategy = dynamic
- 并发线程数 = max(1,CPU核数 * factor)
- factor系数设置:
-
dynamic对应的系数配置项为:junit.jupiter.execution.parallel.config.dynamic.factor - 系数默认值为1
-
#是否允许并行执行
junit.jupiter.execution.parallel.enabled=true
#支持方法级别多线程模式 - same_thread/concurrent
junit.jupiter.execution.parallel.mode.default = same_thread
#支持类级别多线程模式 - same_thread/concurrent
junit.jupiter.execution.parallel.mode.classes.default = concurrent
# dynamic 动态策略
junit.jupiter.execution.parallel.config.strategy = dynamic
junit.jupiter.execution.parallel.config.dynamic.factor=1
(2)fixed 固定策略
- 文件配置策略:junit.jupiter.execution.parallel.config.strategy = fixed
- 并发线程数为 设置的
junit.jupiter.execution.parallel.config.fixed.parallelism的value值
junit.jupiter.execution.parallel.config.strategy = fixed
junit.jupiter.execution.parallel.config.fixed.parallelism=3
(3)custom 自定义策略
- 文件配置策略:
junit.jupiter.execution.parallel.config.strategy = custom
junit.jupiter.execution.parallel.config.class=com.ceshiren.MyCustomStrategy
junit.jupiter.execution.parallel.config.custom.parallelism=3
- 通过实现 ParallelExecutionConfigurationStrategy 接口来配置并行的线程池数量。
- 所需的并行数 使用
ParallelExecutionConfigurationStrategy接口实现。
package com.ceshiren;
import org.junit.platform.commons.JUnitException;
import org.junit.platform.engine.ConfigurationParameters;
import org.junit.platform.engine.support.hierarchical.ParallelExecutionConfiguration;
import org.junit.platform.engine.support.hierarchical.ParallelExecutionConfigurationStrategy;
public class MyCustomStrategy implements ParallelExecutionConfigurationStrategy {
@Override
public ParallelExecutionConfiguration createConfiguration(ConfigurationParameters configurationParameters) {
Integer count = configurationParameters.get("custom.parallelism", Integer::valueOf)
.orElseThrow(() -> {
return new JUnitException(String.format("Configuration parameter '%s' must be set", "fixed.parallelism"));
});
return new ParallelExecutionConfiguration() {
@Override
public int getParallelism() {
return count;
}
@Override
public int getMinimumRunnable() {
return count;
}
@Override
public int getMaxPoolSize() {
return count;
}
@Override
public int getCorePoolSize() {
return count;
}
@Override
public int getKeepAliveSeconds() {
return count;
}
};
}
}
6,并行数据同步
- 背景:测试用例串行(即单线程)的时候,每次传值都能正常断言,但是并行时有时候会断言失败,
Unit5以@ResourceLock注解的形式为我们提供了共享资源的同步机制。
@ResourceLock相当于Java代码中的 synchronized 、@Synchronized
@ResourceLock注解为 测试类 和 测试方法 提供声明式同步机制。
@ResourceLock注解有两个参数
一个是String指定唯一标识共享资源的值,资源值可以是预定义的或用户定义的
一个是ResourceAccessMode指定访问资源的模式,访问模式可以是 READ 「只读」和 READ_WRITE「读和写」(默认是读写模式)
使用预定义资源
-
Resources.SYSTEM_PROPERTIES表示 Java 的系统属性。 -
Resources.SYSTEM_OUT代表当前进程的标准输出流。 -
Resources.SYSTEM_ERR表示当前进程的标准错误流。 -
Resources.LOCALE当前 JVM 实例的默认语言环境。 -
Resources.TIMEZONE当前 JVM 实例的默认时区。
package reourcesLock;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.parallel.Execution;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.parallel.ExecutionMode;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.parallel.ResourceLock;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.parallel.Resources;
import java.util.Properties;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertEquals;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertNull;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.parallel.ExecutionMode.CONCURRENT;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.parallel.ResourceAccessMode.READ;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.parallel.ResourceAccessMode.READ_WRITE;
@Execution(CONCURRENT)
public class RourcesLockTest {
Properties properties;
@BeforeEach
void before(){
properties = new Properties(System.getProperties());
}
@Test
@ResourceLock(value= Resources.SYSTEM_PROPERTIES,mode=READ)
void test1(){
assertNull(System.getProperty("custom properties"));
}
@Test
@ResourceLock(value= Resources.SYSTEM_PROPERTIES,mode=READ_WRITE)
void test2(){
System.setProperty("custom properties","ceshiren");
assertEquals("ceshiren",System.getProperty("custom properties"));
}
@Test
@ResourceLock(value= Resources.SYSTEM_PROPERTIES,mode=READ_WRITE)
void test3(){
System.setProperty("custom properties","hogwarts");
assertEquals("hogwarts",System.getProperty("custom properties"));
}
}
使用用户定义的资源值
- 自定义一个资源
package com.ceshiren.user;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class UserDemo {
static Map<Integer,String> global_user = new HashMap<>();
public static String get(int id){
return global_user.get(id);
};
public static void add(int id,String name){
global_user.put(id,name);
};
public static void update(int id,String name){
global_user.put(id,name);
};
public static void remove(int id){
global_user.remove(id);
};
public static void clear(){
global_user.clear();
};
public static Collection<String> getUser(){
return global_user.values();
}
}
- 使用自定义资源进行资源共享同步
package reourcesLock;
import com.ceshiren.user.UserDemo;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.BeforeEach;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.parallel.Execution;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.parallel.ExecutionMode;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.parallel.ResourceLock;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.parallel.Resources;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.*;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.parallel.ResourceAccessMode.READ;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.parallel.ResourceAccessMode.READ_WRITE;
@Execution(ExecutionMode.CONCURRENT)
public class ResourcesLock2Test {
//这里GLOBALE_USER的值为新增资源的包名+类名+参数名
public static final String GLOBALE_USER = "com.ceshiren.user.UserDemo.name";
@BeforeEach
void before(){
UserDemo.clear();
}
@Test
@ResourceLock(value= GLOBALE_USER,mode=READ)
void test01(){
System.out.println(UserDemo.getUser());
assertTrue( UserDemo.getUser().isEmpty());
}
@Test
@ResourceLock(value= GLOBALE_USER,mode=READ_WRITE)
void test02(){
UserDemo.add(1,"semi");
System.out.println(UserDemo.getUser());
assertEquals("semi",UserDemo.get(1));
}
@Test
@ResourceLock(value= GLOBALE_USER,mode=READ_WRITE)
void test03(){
UserDemo.add(1,"ceshiren");
System.out.println(UserDemo.getUser());
assertEquals("ceshiren",UserDemo.get(1));
}
@Test
@ResourceLock(value= GLOBALE_USER,mode=READ_WRITE)
void test04(){
UserDemo.add(2,"hogwarts");
System.out.println(UserDemo.getUser());
UserDemo.remove(2);
System.out.println(UserDemo.getUser());
assertNull(UserDemo.get(2));
}
}