[TOC]
L1
allure 安装
- 安装 Java,配置环境变量。
- 安装 Allure ,配置环境变量。
- 安装插件
- Python:
pip install allure。 - Java:Maven插件安装。
- Python:
- 执行命令验证环境
allure --version
allure 运行
- 生成测试报告流程
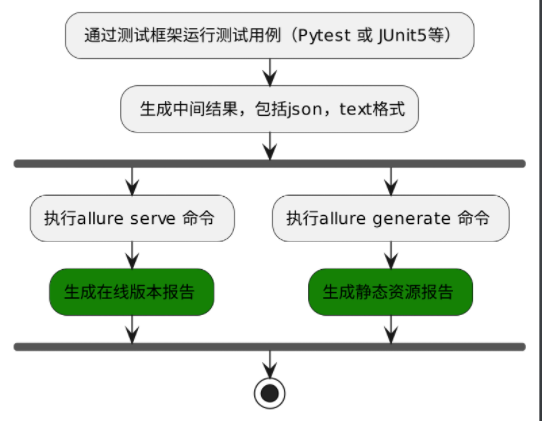
- python下运行 Allure2
# 在测试执行期间收集结果 pytest [测试用例/模块/包] --alluredir=./result/ (—alluredir这个选项 用于指定存储测试结果的路径) # 生成在线的测试报告 allure serve ./result - Java下运行Allure2
# 在测试执行期间收集结果 # mvn命令行使用 maven插件安装 mvn clean test allure:report # 生成在线的测试报告 # mvn 直接找target/allure-results目录 mvn allure:serve
L2
报告生成
- 生成精美报告
- 命令行格式
allure [option] [command] [command options]# 步骤一:在测试执行期间收集结果 # —alluredir这个选项 用于指定存储测试结果的路径 pytest [测试文件] -s –q --alluredir=./result/ # 如果要清除已经生成的报告的历史记录,可以添加参数--clean-alluredir pytest [测试文件] -s –q --alluredir=./result/ --clean-alluredir # 步骤二:查看测试报告,注意这里的serve书写 allure serve ./result/
- 命令行格式
- 在线报告–会直接打开默认浏览器展示当前报告。
allure serve ./result/ (注意这里的serve书写) - 静态报告–希望随时打开报告,可以生成一个静态资源文件报告,将这个报告布署到 web 服务器上,启动 web 服务,即可随时随地打开报告。
# 生成报告
allure generate ./result
# 打开报告
allure open ./report/
- 常用参数
- allure generate 可以指定输出路径,也可以清理上次的报告记录。
-o / –output 输出报告的路径。
-c / –clean 如果报告路径重复。 - allure open 打开报告。
-h / –host 主机 IP 地址,此主机将用于启动报表的 web 服务器。
-p / –port 主机端口,此端口将用于启动报表的 web 服务器,默认值:0。# 生成报告,指定输出路径,清理报告。 allure generate ./result -o ./report --clean # 打开报告,指定IP地址和端口。 allure open -h 127.0.0.1 -p 8883 ./report/
- allure generate 可以指定输出路径,也可以清理上次的报告记录。
添加用例标题
- 用法
| 方法名 | 方法参数 | 参数说明 |
| :------------------------ | :----------------- | :---------------------------------------- |
| @allure.epic() | epic 描述 | 敏捷里面的概念,定义史诗,往下是 feature |
| @allure.feature() | 模块名称 | 功能点的描述,往下是 story |
| @allure.story() | 用户故事 | 用户故事,往下是 title |
| @allure.title(用例的标题) | 用例的标题 | 重命名 html 报告名称 |
| @allure.step() | 操作步骤 | 测试用例的步骤 |
| @allure.testcase() | 测试用例的链接地址 | 对应功能测试用例系统里面的 case |
| @allure.issue() | 缺陷 | 对应缺陷管理系统里面的链接 |
| @allure.description() | 用例描述 | 测试用例的描述 |
| @allure.severity() | 用例等级 | blocker,critical,normal,minor,trivial |
| @allure.link() | 链接 | 定义一个链接,在测试报告展现 |
| @allure.attachment() | 附件 | 报告添加附件 |
-
使用装饰器
@allure.title可以为测试用例自定义一个可阅读性的标题-
直接使用
@allure.title为测试用例自定义标题。import allure import pytest @allure.title("自定义测试用例标题") def test_with_title(): assert True -
@allure.title支持通过占位符的方式传递参数,可以实现测试用例标题参数化,动态生成测试用例标题。import allure import pytest @allure.title("参数化用例标题:参数一:{param1} ,参数二: {param2}") @pytest.mark.parametrize("param1, param2, expected", [ (1, 1, 2), (0.1, 0.3, 0.4) ]) def test_with_parametrize_title(param1, param2, expected): assert param1 + param2 == expected -
allure.dynamic.title动态更新测试用例标题。@allure.title("原始标题") def test_with_dynamic_title(): assert True allure.dynamic.title("更改后的新标题")
-
添加用例步骤
-
使用装饰器定义一个测试步骤,在测试用例中使用。
# 方法一:使用装饰器定义一个测试步骤,在测试用例中使用 import allure import pytest @allure.step def simple_step1(step_param1, step_param2 = None): '''定义一个测试步骤''' print(f"步骤1:打开页面,参数1: {step_param1}, 参数2:{step_param2}") @allure.step def simple_step2(step_param): '''定义一个测试步骤''' print(f"步骤2:完成搜索 {step_param} 功能") @pytest.mark.parametrize('param1', ["pytest", "allure"], ids=['search pytest', 'search allure']) def test_parameterize_with_id(param1): simple_step2(param1) @pytest.mark.parametrize('param1', [True, False]) @pytest.mark.parametrize('param2', ['value 1', 'value 2']) def test_parametrize_with_two_parameters(param1, param2): simple_step1(param1, param2) @pytest.mark.parametrize('param2', ['pytest', 'unittest']) @pytest.mark.parametrize('param1,param3', [[1,2]]) def test_parameterize_with_uneven_value_sets(param1, param2, param3): simple_step1(param1, param3) simple_step2(param2) -
使用
with allure.step()添加测试步骤。# 方法二:使用 `with allure.step()` 添加测试步骤 @allure.title("搜索用例") def test_step_in_method(): with allure.step("测试步骤一:打开页面"): print("操作 a") print("操作 b") with allure.step("测试步骤二:搜索"): print("搜索操作 ") with allure.step("测试步骤三:断言"): assert True
添加用例链接
-
应用场景:将报告与 bug 管理系统或测试用例管理系统集成,可以添加链接装饰器
@allure.link、@allure.issue和@allure.testcase。 -
@allure.link(url, name)添加一个普通的 link 链接。 -
@allure.testcase(url, name)添加一个用例管理系统链接。 -
@allure.issue(url, name),添加 bug 管理系统链接。# 格式1:添加一个普通的link 链接 @allure.link('https://ceshiren.com/t/topic/15860') def test_with_link(): pass # 格式1:添加一个普通的link 链接,添加链接名称 @allure.link('https://ceshiren.com/t/topic/15860', name='这是用例链接地址') def test_with_named_link(): pass # 格式2:添加用例管理系统链接 TEST_CASE_LINK = 'https://github.com/qameta/allure-integrations/issues/8#issuecomment-268313637' @allure.testcase(TEST_CASE_LINK, '用例管理系统') def test_with_testcase_link(): pass # 格式3:添加bug管理系统链接 # 这个装饰器在展示的时候会带 bug 图标的链接。可以在运行时通过参数 `--allure-link-pattern` 指定一个模板链接,以便将其与提供的问题链接类型链接模板一起使用。执行命令需要指定模板链接:`--allure-link-pattern=issue:https://ceshiren.com/t/topic/{}` @allure.issue("15860", 'bug管理系统') def test_with_issue(): pass
添加用例分类
-
应用场景:可以为项目,以及项目下的不同模块对用例进行分类管理。也可以运行某个类别下的用例。
-
报告展示:类别会展示在测试报告的 Behaviors 栏目下。
-
@allure.epic:敏捷里面的概念,定义史诗,往下是 feature。希望在测试报告中看到用例所在的项目,需要用到 epic,相当于定义一个项目的需求,由于粒度比较大,在 epic 下面还要定义略小粒度的用户故事。import allure @allure.epic("需求1") class TestEpic: def test_case1(self): print("用例1") def test_case2(self): print("用例2") def test_case3(self): print("用例3") -
@allure.feature``@allure.story:希望在报告中看到测试功能,子功能或场景。-
功能上加
@allure.feature('功能名称') -
子功能上加
@allure.story('子功能名称')
-
import allure @allure.epic("需求1") @allure.feature("功能模块1") class TestEpic: @allure.story("子功能1") @allure.title("用例1") def test_case1(self): print("用例1") @allure.story("子功能2") @allure.title("用例2") def test_case2(self): print("用例2") @allure.story("子功能2") @allure.title("用例3") def test_case3(self): print("用例3") @allure.story("子功能1") @allure.title("用例4") def test_case4(self): print("用例4") -
-
allure 相关的命令查看 :
pytest --help|grep allure -
通过指定命令行参数,运行 epic/feature/story 相关的用例:
pytest 文件名 --allure-epics=EPICS_SET --allure-features=FEATURES_SET --allure-stories=STORIES_SET# 只运行 epic 名为 "需求1" 的测试用例 pytest --alluredir ./results --clean-alluredir --allure-epics=需求1 # 只运行 feature 名为 "功能模块2" 的测试用例 pytest --alluredir ./results --clean-alluredir --allure-features=功能模块2 # 只运行 story 名为 "子功能1" 的测试用例 pytest --alluredir ./results --clean-alluredir --allure-stories=子功能1 # 运行 story 名为 "子功能1和子功能2" 的测试用例 pytest --alluredir ./results --clean-alluredir --allure-stories=子功能1,子功能2 # 运行 feature + story 的用例(取并集) pytest --alluredir ./results --clean-alluredir --allure-features=功能模块1 --allure-stories=子功能1,子功能2
添加用例描述
-
方式一:使用装饰器
@allure.description()传递一个字符串参数来描述测试用例。@allure.description(""" 多行描述语:<br/> 这是通过传递字符串参数的方式添加的一段描述语,<br/> 使用的是装饰器 @allure.description """) def test_description_provide_string(): assert True -
方式二:使用装饰器
@allure.description_html传递一段 HTML 文本来描述测试用例。@allure.description_html("""html代码块""") def test_description_privide_html(): assert True -
方式三:直接在测试用例方法中通过编写文档注释的方法来添加描述。
def test_description_docstring(): """ 直接在测试用例方法中 </br> 通过编写文档注释的方法 </br> 来添加描述。 </br> :return: """ assert True -
方式四:用例代码内部动态添加描述信息。
import allure @allure.description("""这个描述将被替换""") def test_dynamic_description(): assert 42 == int(6 * 7) allure.dynamic.description('这是最终的描述信息') # allure.dynamic.description_html(''' html 代码块 ''')
添加用例优先级
- 用例执行时,希望按照严重级别执行测试用例,可以为每个用例添加一个等级的装饰器。
@allure.severity - Allure 对严重级别的定义分为 5 个级别:
- Blocker级别:中断缺陷(客户端程序无响应,无法执行下一步操作)。
- Critical级别:临界缺陷( 功能点缺失)。
- Normal级别:普通缺陷(数值计算错误)。
- Minor级别:次要缺陷(界面错误与UI需求不符)。
- Trivial级别:轻微缺陷(必输项无提示,或者提示不规范)。
-
使用装饰器添加用例方法/类的级别。类上添加的级别,对类中没有添加级别的方法生效。
-
运行时添加命令行参数
--allure-severities:pytest --alluredir ./results --clean-alluredir --allure-severities normal,blocker
import allure
def test_with_no_severity_label():
pass
@allure.severity(allure.severity_level.TRIVIAL)
def test_with_trivial_severity():
pass
@allure.severity(allure.severity_level.NORMAL)
def test_with_normal_severity():
pass
@allure.severity(allure.severity_level.NORMAL)
class TestClassWithNormalSeverity(object):
def test_inside_the_normal(self):
pass
@allure.severity(allure.severity_level.CRITICAL)
def test_critical_severity(self):
pass
@allure.severity(allure.severity_level.BLOCKER)
def test_blocker_severity(self):
pass
添加tags标签
-
Allure 报告支持的一些常见 Pytest 特性包括 xfail、skipif、fixture 等
-
使用装饰器
@pytest.xfail()、@pytest.skipif()import pytest # 当用例通过时标注为 xfail @pytest.mark.xfail(condition=lambda: True, reason='这是一个预期失败的用例') def test_xfail_expected_failure(): """this test is an xfail that will be marked as expected failure""" assert False # 当用例通过时标注为 xpass @pytest.mark.xfail def test_xfail_unexpected_pass(): """this test is an xfail that will be marked as unexpected success""" assert True # 跳过用例 @pytest.mark.skipif('2 + 2 != 5', reason='当条件触发时这个用例被跳过 @pytest.mark.skipif') def test_skip_by_triggered_condition(): pass -
fixture 和 finalizer 是分别在测试开始之前和测试结束之后由 Pytest 调用的实用程序函数。Allure 跟踪每个 fixture 的调用,并详细显示调用了哪些方法以及哪些参数,从而保持了调用的正确顺序。
import pytest @pytest.fixture() def func(request): print("这是一个fixture方法") # 定义一个终结器,teardown动作放在终结器中 def over(): print("session级别终结器") request.addfinalizer(over) class TestClass(object): def test_with_scoped_finalizers(self,func): print("测试用例")
失败重试
-
Allure 可以收集用例运行期间,重试的用例的结果,以及这段时间重试的历史记录。
-
重试功能可以使用 pytest 相关的插件,例如
pytest-rerunfailures。 -
重试的结果信息,会展示在详情页面的”Retries” 选项卡中。
import pytest @pytest.mark.flaky(reruns=2, reruns_delay=2) def test_rerun2(): assert False
L3
添加附件–图片
-
在做 UI 自动化测试时,可以将页面截图,或者出错的页面进行截图,将截图添加到测试报告中展示,辅助定位问题
-
支持添加的附件类型
TEXT = ("text/plain", "txt") CSV = ("text/csv", "csv") TSV = ("text/tab-separated-values", "tsv") URI_LIST = ("text/uri-list", "uri") HTML = ("text/html", "html") XML = ("application/xml", "xml") JSON = ("application/json", "json") YAML = ("application/yaml", "yaml") PCAP = ("application/vnd.tcpdump.pcap", "pcap") PNG = ("image/png", "png") JPG = ("image/jpg", "jpg") SVG = ("image/svg-xml", "svg") GIF = ("image/gif", "gif") BMP = ("image/bmp", "bmp") TIFF = ("image/tiff", "tiff") MP4 = ("video/mp4", "mp4") OGG = ("video/ogg", "ogg") WEBM = ("video/webm", "webm") PDF = ("application/pdf", "pdf") -
python中添加图片
-
allure.attach.file(source, name, attachment_type, extension),参数解释:- source:文件路径,相当于传一个文件。
- name:附件名字。
- attachment_type:附件类型,是
allure.attachment_type其中的一种(支持 PNG、JPG、BMP、GIF 等)。 - extension:附件的扩展名。
mport allure class TestWithAttach: def test_pic(self): allure.attach.file("pic.png", name="图片", attachment_type=allure.attachment_type.PNG, extension="png")-
allure.attach(body, name=None, attachment_type=None, extension=None):,参数解释:- body:要写入附件的内容
- name:附件名字。
- attachment_type:附件类型,是
allure.attachment_type其中的一种(支持 PNG、JPG、BMP、GIF 等)。 - extension:附件的扩展名。
import allure class TestWithAttach: def test_pic2(self): with open("./img/logo.png",mode="rb") as f : file = f.read() allure.attach(file,"页面截图",allure.attachment_type.PNG) -
-
Java中添加图片
-
注解方式直接传入图片
@Attachment(value = "图片名", type = "image/png", fileExtension = "后缀") -
使用Allure方法传入图片
Allure.addAttachment("图片名", "image/png", 图片路径, "后缀");
-
-
裂图的原因以及解决办法
-
图片上传过程中出现了网络中断或者传输过程中出现了错误:重新上传图片。
-
Allure 报告中的图片大小超过了 Allure 的限制: 调整图片大小。
-
图片本身存在问题:检查图片格式和文件本身
-
添加附件–日志
-
Python:使用 python 自带的 logging 模块生成日志,日志会自动添加到测试报告中。
-
日志配置,在测试报告中使用
logger对象生成对应级别的日志。# 创建一个日志模块: log_util.py import logging import os from logging.handlers import RotatingFileHandler # 绑定绑定句柄到logger对象 logger = logging.getLogger(__name__) # 获取当前工具文件所在的路径 root_path = os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__)) # 拼接当前要输出日志的路径 log_dir_path = os.sep.join([root_path, f'/logs']) if not os.path.isdir(log_dir_path): os.mkdir(log_dir_path) # 创建日志记录器,指明日志保存路径,每个日志的大小,保存日志的上限 file_log_handler = RotatingFileHandler(os.sep.join([log_dir_path, 'log.log']), maxBytes=1024 * 1024, backupCount=10 , encoding="utf-8") # 设置日志的格式 date_string = '%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S' formatter = logging.Formatter( '[%(asctime)s] [%(levelname)s] [%(filename)s]/[line: %(lineno)d]/[%(funcName)s] %(message)s ', date_string) # 日志输出到控制台的句柄 stream_handler = logging.StreamHandler() # 将日志记录器指定日志的格式 file_log_handler.setFormatter(formatter) stream_handler.setFormatter(formatter) # 为全局的日志工具对象添加日志记录器 # 绑定绑定句柄到logger对象 logger.addHandler(stream_handler) logger.addHandler(file_log_handler) # 设置日志输出级别 logger.setLevel(level=logging.INFO) -
代码输出到用例详情页面。
-
运行用例:
pytest --alluredir ./results --clean-alluredir(注意不要加-vs)。class TestWithLogger: @allure.story("子功能1") @allure.title("用例1") def test_case1(self): logger.info("用例1的 info 级别的日志") logger.debug("用例1的 debug 级别的日志") logger.warning("用例1的 warning 级别的日志") logger.error("用例1的 error 级别的日志") logger.fatal("用例1的 fatal 级别的日志") -
日志展示在 Test body 标签下,标签下可展示多个子标签代表不同的日志输出渠道:
- log 子标签:展示日志信息。
- stdout 子标签:展示 print 信息。
- stderr 子标签:展示终端输出的信息。
-
禁用日志,可以使用命令行参数控制
--allure-no-capturepytest --alluredir ./results --clean-alluredir --allure-no-capture
-
-
Java:直接通过注解或调用方法添加。
- 注解方式添加
- 调用方法添加
添加附件–html
-
可以定制测试报告页面效果,可以将 HTML 类型的附件显示在报告页面上。
-
python使用
allure.attach()添加 html 代码。allure.attach(body, name, attachment_type, extension),参数解释:- body:要写入附件的内容(HTML 代码块)。
- name:附件名字。
- attachment_type:附件类型,是
allure.attachment_type其中的一种。 - extension:附件的扩展名。
class TestWithAttach: def test_html(self): allure.attach('<head></head><body> a page </body>', '附件是HTML类型', allure.attachment_type.HTML) def test_html_part(self): allure.attach('''html代码块''', '附件是HTML类型', allure.attachment_type.HTML) -
Java:直接通过注解或调用方法添加。
-
注解方式
@Attachment(value = "html名", type = "text/html", fileExtension = "后缀") 调用方法添加 - Java 使用Allure方法传入html。 Allure.addAttachment("html名", "text/html", 图片路径, "后缀"); -
使用Allure方法传入html
Allure.addAttachment("html名", "text/html", 图片路径, "后缀");
-
添加附件–视频
在做 UI 自动化测试时,可以将页面截图,或者出错的页面进行截图,将截图添加到测试报告中展示,辅助定位问题。
-
Python:使用
allure.attach.file()添加视频。语法:
allure.attach.file(source, name, attachment_type, extension)参数解释:
-
source:文件路径,相当于传一个文件。
-
name:附件名字。
-
attachment_type:附件类型,是
allure.attachment_type其中的一种。 -
extension:附件的扩展名。
import allure class TestWithAttach: def test_video(self): allure.attach.file("xxx.mp4", name="视频", attachment_type=allure.attachment_type.MP4, extension="mp4")
-
-
Java:直接通过注解或调用方法添加。
-
注解方式直接传入视频
@Attachment(value = "视频名", type = "video/mp4", fileExtension = "后缀") 调用方法添加 - Java 使用Allure方法传入视频。 Allure.addAttachment("视频名", "video/mp4", 视频路径, "后缀"); -
调用方法
Allure.addAttachment("视频名", "video/mp4", 视频路径, "后缀");
-
L4
报告定制
针对不同的项目可能需要对测试报告展示的效果进行定制,比如修改页面的 logo、修改项目的标题或者添加一些定制的功能等等。
-
定制logo
-
修改
allure.yml文件,添加 logo 插件custom-logo-plugin(在 allure 安装路径下,可以通过where allure或者which allure查看 allure 安装路径)。 -
编辑 styles.css 文件,配置 logo 图片。
-
/* 打开 styles.css 文件,
目录在:/xxx/allure-2.13.2/plugins/custom-logo-plugin/static/styles.css,
将内容修改为:*/
.side-nav__brand {
background: url("logo.png") no-repeat left center !important;
margin-left: 10px;
height: 40px;
background-size: contain !important;
}
-
定制页面标题
编辑 styles.css 文件,添加修改标题对应的代码。
/* 去掉图片后边 allure 文本 */ .side-nav__brand-text { display: none; } /* 设置logo 后面的字体样式与字体大小 */ .side-nav__brand:after { content: "霍格沃兹测试学社"; margin-left: 18px; height: 20px; font-family: Arial; font-size: 13px; }
