1、Fixture 用法
Fixture 特点及优势
- 1、命令灵活:对于 setup,teardown,可以不起这两个名字
- 2、数据共享:在 conftest.py 配置⾥写⽅法可以实现数据共享,不需要 import 导⼊。可以跨⽂件共享
- 3、scope 的层次及神奇的 yield 组合相当于各种 setup 和 teardown
- 4、实现参数化
Fixture 在自动化中的应用- 基本用法
- 场景:
测试⽤例执⾏时,有的⽤例需要登陆才能执⾏,有些⽤例不需要登陆。
通常用上面的方法,但是pytest有更简单的实现方式
setup 和 teardown ⽆法满⾜。fixture 可以。默认 scope(范围)function
-
步骤:
- 1.导⼊ pytest
- 2.在登陆的函数上⾯加@pytest.fixture()
- 3.在要使⽤的测试⽅法中传⼊(登陆函数名称),就先登陆
- 4.不传⼊的就不登陆直接执⾏测试⽅法。
import pytest
# 定义了登录的fixture
@pytest.fixture()
def login():
print("完成登录操作")
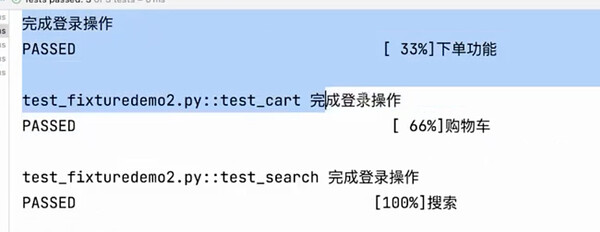
def test_search():
print("搜索")
# 传入登陆函数名称,执行用例的时候会先完成登录操作,在执行用例
def test_cart(login):
print("购物车")
def test_order(login):
print("下单功能")
Fixture 在自动化中的应用 - 作用域
| 取值 | 范围 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| function | 函数级 | 每一个函数或方法都会调用(默认函数级别) |
| class | 类级别 | 每个测试类只运行一次 |
| module | 模块级 | 每一个.py 文件调用一次 |
| package | 包级 | 每一个 python 包只调用一次(暂不支持) |
| session | 会话级 | 每次会话只需要运行一次,会话内所有方法及类,模块都共享这个方法 |
一个会话指pytest运行起来后,就是一个会话,运行的整个项目就是一个会话
import pytest
# 定义了登录的fixture尽量避免以test_开头
# 默认函数级别
@pytest.fixture()
def login():
print("完成登录操作")
def test_search(login):
print("搜索")
def test_cart(login):
print("购物车")
def test_order(login):
print("下单功能")
默认函数级别-每个函数执行前都会执行
import pytest
# 定义了登录的fixture,尽量避免以test_开头
# 默认函数级别,改为模块级别
@pytest.fixture(scppe="module")
def login():
print("完成登录操作")
def test_search(login):
print("搜索")
def test_cart(login):
print("购物车")
def test_order(login):
print("下单功能")
整个模块.py文件,所有用例执行之前执行。
Fixture 在自动化中的应用 - yield 关键字
- 场景:
你已经可以将测试⽅法【前要执⾏的或依赖的】解决了,
测试⽅法后销毁清除数据的要如何进⾏呢?
- 解决:
通过在 fixture 函数中加⼊ yield 关键字,yield 是调⽤第⼀次返回结果,
第⼆次执⾏它下⾯的语句返回。
- 步骤:
在@pytest.fixture(scope=module)。
在登陆的⽅法中加 yield,之后加销毁清除的步骤
# fixture 的作用域
import pytest
# 定义了登录的fixture,尽量避免以test_开头
"""
@pytest.fixture
def fixture_name():
setup 操作
yield 返回值
teardown 操作
"""
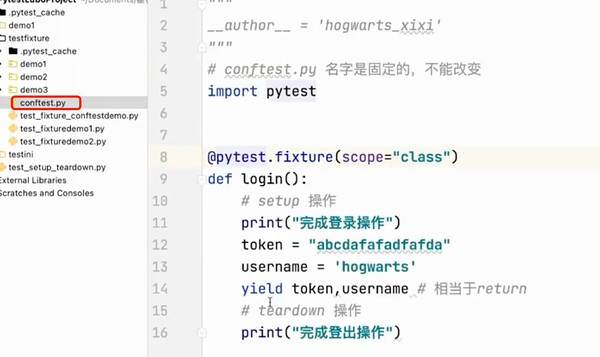
@pytest.fixture(scope="class")
def login():
# setup 操作
print("完成登录操作")
token = "abcdafafadfafda"
username = 'hogwarts'
yield token,username # 相当于return
# teardown 操作
print("完成登出操作")
def test_search(login):
token,username = login
print(f"token:{token} , name : {username}")
# login 返回 None,方法不加return,默认返回None
print("搜索")
def test_cart(login):
print("购物车")
def test_order(login):
print("下单功能")
class TestDemo:
def test_case1(self,login):
print("case1")
def test_case2(self,login):
print("case2")
Fixture 在自动化中的应用 - 数据共享
- 场景:
你与其他测试⼯程师合作⼀起开发时,公共的模块要在不同⽂件中,要在⼤家都访问到的地⽅。
- 解决:
使⽤ conftest.py 这个⽂件进⾏数据共享,并且他可以放在不同位置起着不同的范围共享作⽤。
-
前提:
- conftest ⽂件名是不能换的
- 放在项⽬下是全局的数据共享的地⽅
-
执⾏:
- 系统执⾏到参数 login 时先从本模块中查找是否有这个名字的变量什么的,
- 之后在 conftest.py 中找是否有。
- 步骤:
将登陆模块带@pytest.fixture 写在 conftest.py
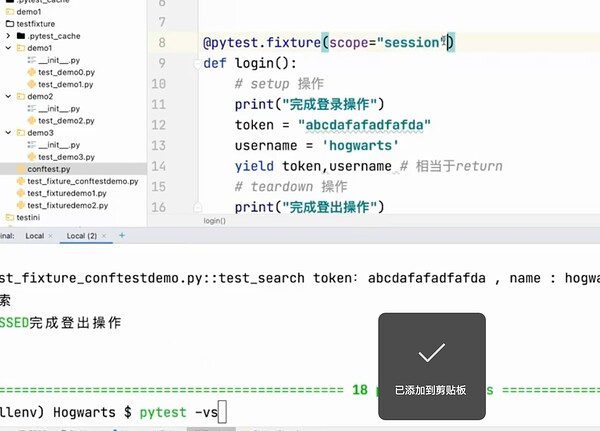
# conftest.py 名字是固定的,不能改变
import pytest
@pytest.fixture(scope="function")
def login():
# setup 操作
print("完成登录操作")
token = "abcdafafadfafda"
username = 'hogwarts'
yield token,username # 相当于return
# teardown 操作
print("完成登出操作")
如果设置session会话级别,整个运行期间只调用一次
所有用例都添加login后,运行所有用例,只运行了一次
Fixture 在自动化中的应用 - 自动应用
场景:
不想原测试⽅法有任何改动,或全部都⾃动实现⾃动应⽤,
没特例,也都不需要返回值时可以选择⾃动应⽤
解决:
使⽤ fixture 中参数 autouse=True 实现
步骤:
在⽅法上⾯加 @pytest.fixture(autouse=True)
# conftest.py 名字是固定的,不能改变
import pytest
@pytest.fixture(scope="function",autouse=True)
def login():
# setup 操作
print("完成登录操作")
token = "abcdafafadfafda"
username = 'hogwarts'
yield token,username # 相当于return
# teardown 操作
print("完成登出操作")
Fixture 在自动化中的应用 -参数化
场景:
测试离不开数据,为了数据灵活,⼀般数据都是通过参数传的
解决:
fixture 通过固定参数 request 传递
步骤:
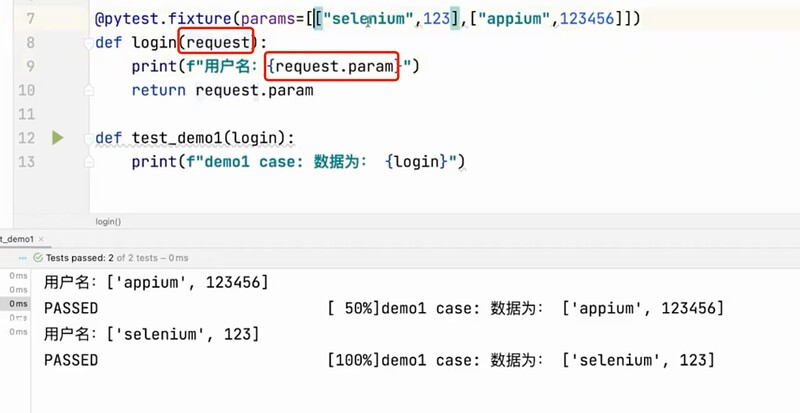
在 fixture 中增加@pytest.fixture(params=[1, 2, 3, ‘linda’])
在⽅法参数写 request,方法体里面使用 request.param 接收参数
import pytest
@pytest.fixture(params=[["selenium",123],["appium",123456]])
def login(request):
print(f"用户名:{request.param}")
return request.param
def test_demo1(login):
print(f"demo1 case: 数据为: {login}")
Fixture 的用法总结
- 模拟 setup,teardown(一个用例可以引用多个 fixture)
- yield 的用法
- 作用域( session,module, 类级别,方法级别 )
- 自动执行 (autouse 参数)
- conftest.py 用法,一般会把 fixture 写在 conftest.py 文件中(这个文件名字是固定的,不能改)
- 实现参数化