1、pytest 运行用例
运行用例
运行多条用例
- 运行 某个/多个 用例包
- 运行 某个/多个 用例模块
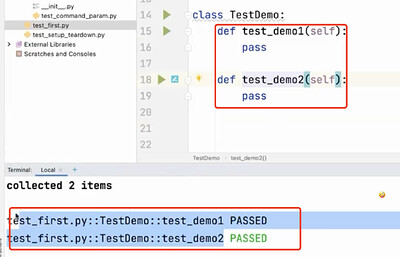
- 运行 某个/多个 用例类
- 运行 某个/多个 用例方法
运行多条用例方式
- 执行包下所有的用例:
pytest/py.test [包名] - 执行单独一个 pytest 模块:
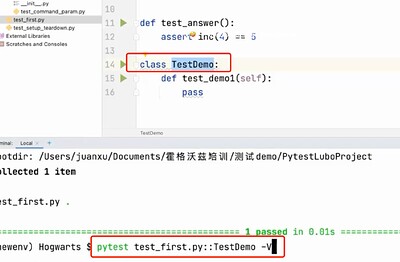
pytest 文件名.py - 运行某个模块里面某个类:
pytest 文件名.py::类名 - 运行某个模块里面某个类里面的方法:
pytest 文件名.py::类名::方法名
pytest 执行当前目录及子目录下所有符合条件的测试用例
执行单独一个 pytest 模块
执行某个类,加-v展示具体执行的哪个
运行结果分析
- 常用的:fail/error/pass
- 特殊的结果:warning/deselect(后面会讲)
2、pytest 测试用例调度与运行
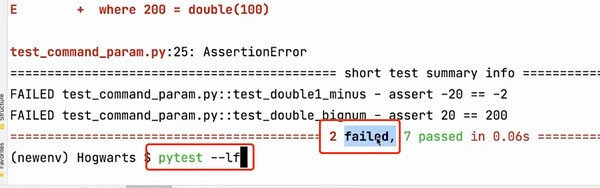
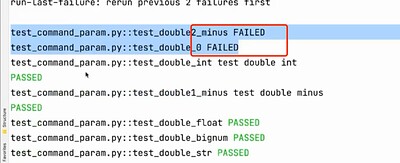
命令行参数-使用缓存状态
-
--lf(--last-failed)只重新运行故障。 -
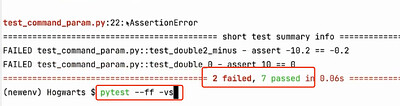
--ff(--failed-first)先运行故障然后再运行其余的测试
只运行上次失败的用例,如果上次没有失败的就全部运行
失败的在中间
先执行失败的,在执行其他的
3、常用命令行参数
命令行参数 - 常用命令行参数
—help
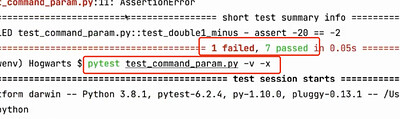
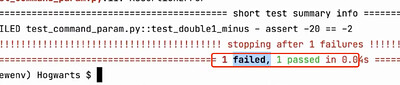
-x 用例一旦失败(fail/error),就立刻停止执行
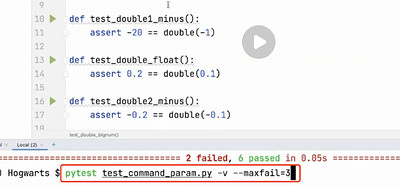
--maxfail=num 用例达到
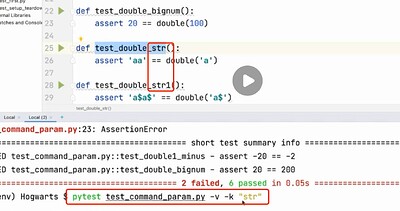
-m 标记用例
-k 执行包含某个关键字的测试用例
-v 打印详细日志
-s 打印输出日志(一般-vs一块儿使用)
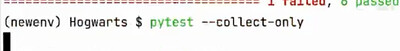
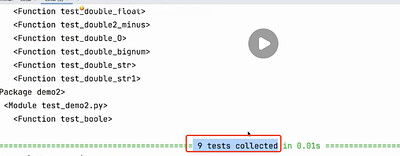
—collect-only(测试平台,pytest 自动导入功能 )
有失败的,其他不执行就加-x
发现失败的就停止执行了,第二条失败了,后面都不执行了
最多可以有几个错误用例数,达到后就停止执行了
运行名字中包含str的用例
其他用例未被命中
只收集不运行
4、python 执行 pytest
Python 代码执行 pytest
- 使用 main 函数
- 使用 python -m pytest 调用 pytest(jenkins 持续集成用到)
Python 代码执行 pytest - main 函数
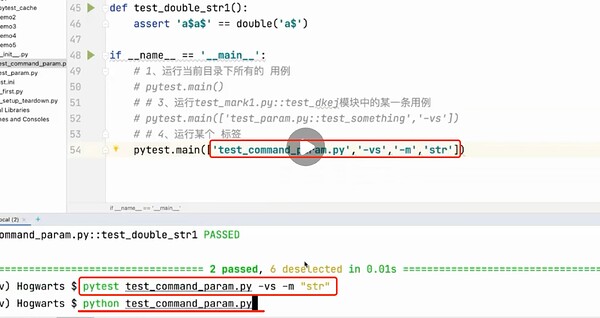
if __name__ == '__main__':
# 1、运行当前目录下所有符合规则的用例,包括子目录(test_*.py 和 *_test.py)
pytest.main()
# 2、运行test_mark1.py::test_dkej模块中的某一条用例
pytest.main(['test_mark1.py::test_dkej','-vs'])
# 3、运行某个 标签
pytest.main(['test_mark1.py','-vs','-m','dkej'])
运行方式
`python test_*.py `
在main里面设置完后,直接用python执行对应模块,相当于在命令行中执行pytest
另一种执行方式,命令行中在pytest前面输入python -m
5、pytest 异常处理
常用的异常处理方法
- try…except
- pytest.raises()
异常处理方法 try …except
try:
可能产生异常的代码块
except [ (Error1, Error2, ... ) [as e] ]:
处理异常的代码块1
except [ (Error3, Error4, ... ) [as e] ]:
处理异常的代码块2
except [Exception]:
处理其它异常
异常处理方法 pytest.raise()
- 可以捕获特定的异常
- 获取捕获的异常的细节(异常类型,异常信息)
- 发生异常,后面的代码将不会被执行
pytest.raise() 用法
异常处理方法 pytest.raise()
def test_raise():
with pytest.raises(ValueError, match='must be 0 or None'):
raise ValueError("value must be 0 or None")
def test_raise1():
with pytest.raises(ValueError) as exc_info:
raise ValueError("value must be 42")
assert exc_info.type is ValueError
assert exc_info.value.args[0] == "value must be 42"