http://doc.pytest.org/en/latest/fixture.html#fixture
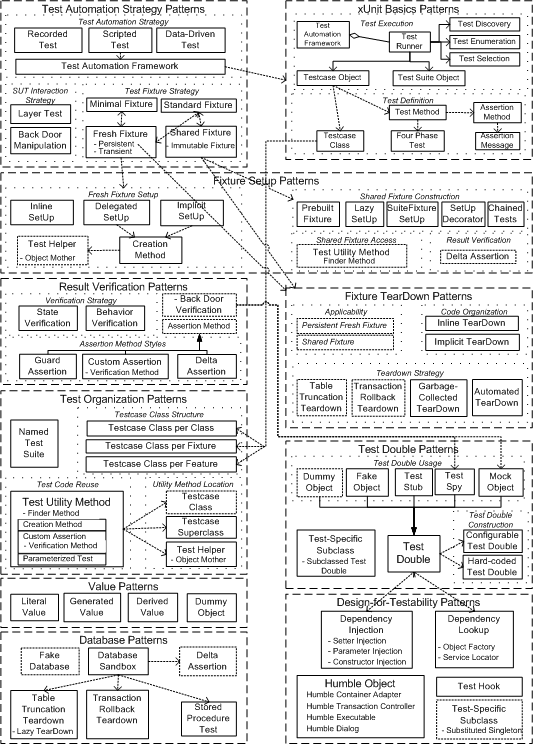
Fixture Setup Patterns at XUnitPatterns.com
pytest 的 fixtures 基于 xUnit 的 setup/teardown 风格,可对测试进行前置处理和后置处理,以下图片是对 xUnit 风格的总结,详细可以参考上面链接:
pytest 的 fixtures 特点如下:
- fixtures 有显式名字:可从测试函数,模块,类或者整个项目中直接调用 fixture
- fixtures 采用模块化:每个 fixture 名字都会调用一个 fixture 函数,该函数也可以调用其他 fixtures
- fixtures 管理从简单的单元扩展到复杂的功能测试,允许根据配置和组件选项对 fixture 和测试进行参数化,或者跨功能、类、模块或整个测试会话范围重用 fixture 。
pytest 支持 classic xunit-style setup 。可以混合这两种样式,从经典样式递增到新样式。也可以使用现有的 unittest.TestCase style 样式或基于 nose 的项目开始。
可以使用 @pytest.fixture 装饰器定义 Fixtures ,比如 官方链接。Pytest 也提供许多内置的 fixtures,以下是简述,后面会进行详解 :
捕获为文本,输出到文件描述符 “1” 和 “2” 。
Capture, as bytes, output to file descriptors 1 and 2 .
Control logging and access log entries.
Capture, as text, output to sys.stdout and sys.stderr .
Capture, as bytes, output to sys.stdout and sys.stderr .
Store and retrieve values across pytest runs.
Provide a dict injected into the docstests namespace.
Temporarily modify classes, functions, dictionaries, os.environ , and other objects.
Access to configuration values, pluginmanager and plugin hooks.
Add extra properties to the test.
Add extra properties to the test suite.
Record warnings emitted by test functions.
Provide information on the executing test function.
Provide a temporary test directory to aid in running, and testing, pytest plugins.
Provide a pathlib.Path object to a temporary directory which is unique to each test function.
Make session-scoped temporary directories and return pathlib.Path objects.
Provide a py.path.local object to a temporary directory which is unique to each test function; replaced by tmp_path .
Make session-scoped temporary directories and return py.path.local objects; replaced by tmp_path_factory .
Fixtures 作为函数参数
测试函数将 fixtures 命名为输入参数,从而来接收它们。 对于每个参数名,与该参数名同名的 fixtures 函数会提供 fixture 对象。 可以用 @pytest.fixture 来注册 fixture 函数。 比如下面例子:
import pytest
@pytest.fixture
def smtp_connection():
import smtplib
return smtplib.SMTP("smtp.gmail.com", 587, timeout=5)
def test_ehlo(smtp_connection):
response, msg = smtp_connection.ehlo()
assert response == 250
assert 0 # for demo purposes
test_ehlo 需要 smtp_connection fixture 的值。 pytest 会发现用 @pytest.fixture 标记的 smtp_connection fixture 函数,运行测试结果如下:
$ pytest test_smtpsimple.py
=========================== test session starts ============================
platform linux -- Python 3.x.y, pytest-5.x.y, py-1.x.y, pluggy-0.x.y
cachedir: $PYTHON_PREFIX/.pytest_cache
rootdir: $REGENDOC_TMPDIR
collected 1 item
test_smtpsimple.py F [100%]
================================= FAILURES =================================
________________________________ test_ehlo _________________________________
smtp_connection = <smtplib.SMTP object at 0xdeadbeef>
def test_ehlo(smtp_connection):
response, msg = smtp_connection.ehlo()
assert response == 250
> assert 0 # for demo purposes
E assert 0
test_smtpsimple.py:14: AssertionError
========================= short test summary info ==========================
FAILED test_smtpsimple.py::test_ehlo - assert 0
从错误信息可以看出,测试函数需要 smtp_connection 参数, fixture 函数创建了 smtplib.SMTP() 实例,因为代码中是 assert 0 ,所以运行会失败,整个调用流程如下:
- pytest发现测试函数 test_ehlo ,由于测试函数需要 smtp_connection 参数,存在与这个参数同名的 fixture 函数。
- 调用
smtp_connection()函数创建实例 - 最终调用
test_ehlo(<smtp_connection instance>)函数
如果拼写了错误的函数参数或者这个参数不可用, pytest 会报错,并列出可用的参数。也可以在命令行用 --fixtures 列出所有可用的 fixtures (包括系统内置的 fixture 和用户自定义的 fixture ),考虑以下代码及执行结果:
import pytest
@pytest.fixture()
def get_10():
return 10
def test_fixture(get_10):
print(get_10)
使用命令 pytest --fixtures 后,输出结果只截取自己的 fixture ,系统内置的 fixture 没有截取:
加上 -v 参数可以展示详细信息,包括 fixture 位置,比如执行 pytest --fixtures -v
Fixtrues: 依赖注入
fixtures 允许测试函数接收初始化后的对象,而不必关心导入/设置/清理的详细信息。这就是依赖注入模式,了解 spring 的同学应该不陌生, spring 用它解决了组件的依赖项和组件之间的过度耦合问题,在 pytest 也是同理。有关依赖注入的详细内容,可查看 wiki :
conftest.py:共享 fixture 函数
有时想在多个测试文件中使用 fixture 函数,就要把 fixture 函数移动到 conftest.py 文件中。 pytest 会自动发现 conftest.py ,你不用手动导入, 发现规则有前有后,依次是类,测试模块,然后是 conftest.py 文件,内置或者第三方插件。
conftest.py 还可以实现 local per-directory plugins 。
考虑以下目录结构及代码内容:
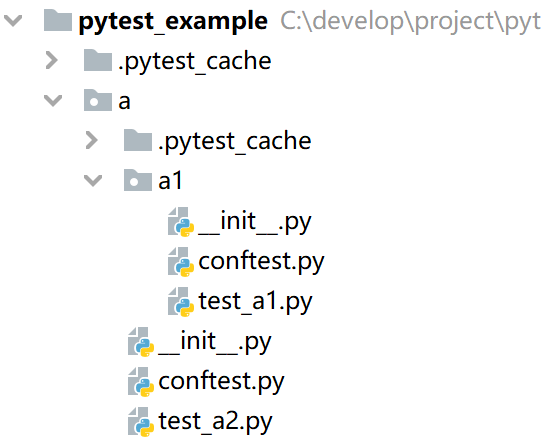
# a/conftest.py文件内容
import pytest
@pytest.fixture()
def tmp():
return 20
# a/a1/conftest.py文件内容
import pytest
@pytest.fixture()
def tmp():
return 30
# test_a1.py文件内容
def test_print(tmp):
print(tmp)
# test_a2.py文件内容
def test_print(tmp):
print(tmp)
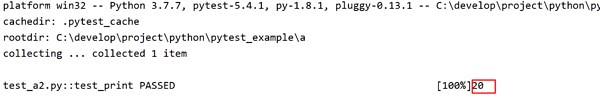
可以看出, pytest_a1.py 输出结果是 30 , pytest_a2.py 输出结果是 20 ,子目录的 conftest.py 内容会覆盖父目录的 conftest.py :
共享测试数据
如果让测试数据多文件可用,最好把数据放到 fixture 中,这个方法充分利用了 pytest 的自动缓存机制。另一个好方法是把数据移动到 tests 目录,社区提供一些插件帮助管理,比如 pytest-datadir 和 pytest-datafiles。
范围:在类,模块或者会话中共享 fixture
在 @pytest.fixture 参数中添加 scope="module" ,使其装饰的函数,仅在每个测试模块中实例化一次(默认在每个测试函数前实例化一次),你可以自行打印 fixture 对象,对比区别。比如下面的 smtplib.SMTP ,会创建一个实例,由于它非常依赖网络,所以设置为模块级别可以避免多次创建。 scope 还有更多的值: function , class , module , package 或者 session 。
接下来的例子把 fixture 放到了 conftest.py 文件,所以目录中的多个测试模块都能访问这个函数:
# content of conftest.py
import pytest
import smtplib
@pytest.fixture(scope="module")
def smtp_connection():
return smtplib.SMTP("smtp.gmail.com", 587, timeout=5)
你可以在 conftest.py 的同目录,或者子目录的测试文件中调用 fixture ,比如下面代码:
# content of test_module.py
def test_ehlo(smtp_connection):
response, msg = smtp_connection.ehlo()
assert response == 250
assert b"smtp.gmail.com" in msg
assert 0 # for demo purposes
def test_noop(smtp_connection):
response, msg = smtp_connection.noop()
assert response == 250
assert 0 # for demo purposes
下面是执行结果,我们故意让其出错( assert 0 ),以便 pytest 可以打印详细信息:
$ pytest test_module.py
=========================== test session starts ============================
platform linux -- Python 3.x.y, pytest-5.x.y, py-1.x.y, pluggy-0.x.y
cachedir: $PYTHON_PREFIX/.pytest_cache
rootdir: $REGENDOC_TMPDIR
collected 2 items
test_module.py FF [100%]
================================= FAILURES =================================
________________________________ test_ehlo _________________________________
smtp_connection = <smtplib.SMTP object at 0xdeadbeef>
def test_ehlo(smtp_connection):
response, msg = smtp_connection.ehlo()
assert response == 250
assert b"smtp.gmail.com" in msg
> assert 0 # for demo purposes
E assert 0
test_module.py:7: AssertionError
________________________________ test_noop _________________________________
smtp_connection = <smtplib.SMTP object at 0xdeadbeef>
def test_noop(smtp_connection):
response, msg = smtp_connection.noop()
assert response == 250
> assert 0 # for demo purposes
E assert 0
test_module.py:13: AssertionError
========================= short test summary info ==========================
FAILED test_module.py::test_ehlo - assert 0
FAILED test_module.py::test_noop - assert 0
============================ 2 failed in 0.12s =============================
assert 0 让 pytest 展示接收到的 smtp_connection 对象,这两个测试函数使用相同的 smtp_connection 对象,即 smtp_connection 只会在整个模块初始化一次。你也可以把 scope 改为 session 级别:
pytest.fixture(scope="session")
def smtp_connection():
# the returned fixture value will be shared for
# all tests needing it
...
fixture的作用范围
session>module>class>function
-
function:每一个函数或方法都会调用
-
class:每一个类调用一次,一个类中可以有多个方法
-
module:每一个 *.py 文件调用一次,该文件内又有多个 function 和 class
-
session:是多个文件调用一次,可以跨 *.py 文件调用,每个 *.py 文件就是 module
注意:
Pytest 同一时间只会缓存一个 fixture ,当使用参数化的 fixture 时, pytest 会在范围内多次调用 fixture 。 pytest3.7 有包范围,由于是测试版,不建议使用。
动态范围
有时,你不想改写代码,做到动态的改变 fixture 范围。可以定义函数,将之传递给 fixture 的 scope 参数,在 fixture 定义的时候会自动执行这个函数。这个函数必须有两个参数 - fixture_name 字符串 和 config 配置对象。
比如下面生成 docker 容器函数 ,你可以使用命令行参数控制范围:
# conftest.py 内容
from time import sleep
import pytest
def determine_scope(fixture_name, config):
# 如果发现参数是 --keep-containers
if config.getoption("--scope_session", None):
return "session"
# 返回函数级别
return "function"
@pytest.fixture(scope=determine_scope)
def create_value():
sleep(5)
def pytest_addoption(parser):
parser.addoption("--scope_session", action="store", default=None,
help="None")
# test_a1内容
def test_a1(create_value):
print('a1')
def test_a2(create_value):
print('a2')
def test_a3(create_value):
print('a3')
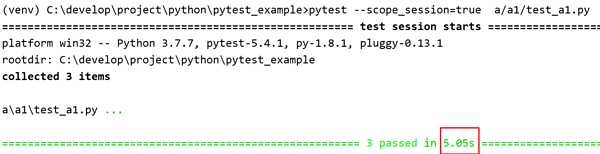
参考以下两种运行结果,加入参数的话, fixture 的范围会被更改成 session 级别, 3 个 test 只会初始化一次 fixture 函数,运行时间为 5s 左右:
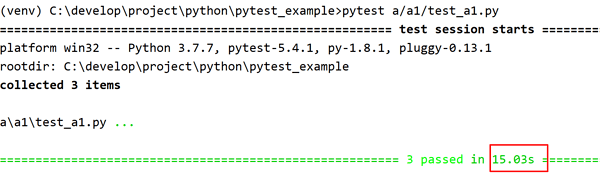
如果没有参数, fixture 的范围会被更改成 function 级别, 3 个 test 会初始化三次 fixture 函数,运行时间为 15s 左右:
顺序:优先实例化高级别范围的 fixture
todo