删除list 里面的重复元素 并保持顺序不变化
例 [1,2,4,2,4,3] 变成 [1,2,4,3]
nums_list = [1,2,4,2,4,3]
res_list =
for i in nums_list:
if i not in res_list:
res_list.append(i)
set强转会改变顺序
是的 没注意到 
用列表推导式比较方便。
list1=[1,2,4,2,4,3]
list2=[list2.append(i) for i in list1 if i not in list2]
print(list2)
list3 = [1,2,4,2,4,3]
list3.reverse()
for i in list3:
for _ in range(list3.count(i)):
if list3.count(i) > 1:
list3.remove(i)
list3.reverse()
"""
删除list 里面的重复元素 并保持顺序不变化
例 [1,2,4,2,4,3] 变成 [1,2,4,3]
"""
def test(test_list: list):
i = 0
while i < len(test_list):
if test_list[i] in test_list[0:i]:
test_list.pop(i)
else:
i += 1
return test_list
assert test([1, 2, 4, 2, 4, 3]) == [1, 2, 4, 3]
assert test([1, 2, 2, 2, 2, 1]) == [1, 2]
assert test([]) == []
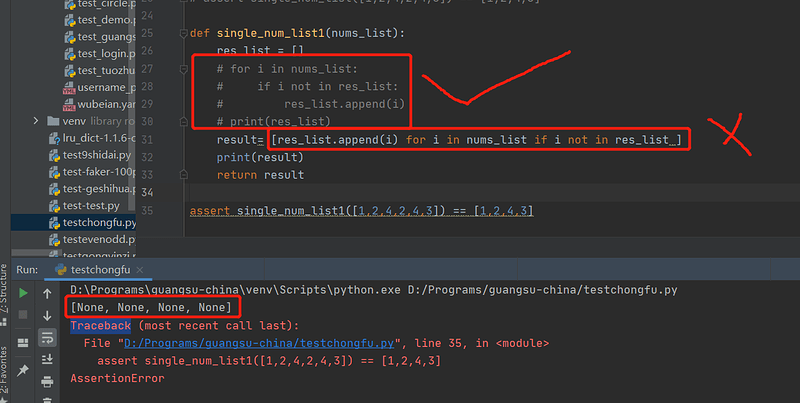
解法1: 列表中都是纯数字。
def single_num_list(li):
return sorted(set(li), key=lambda x:li.index(x))
assert single_num_list([1,2,4,2,4,3]) == [1,2,4,3]
解法2: 凡是列表中的对象是可散列的都适用。例如数字,字符串和元组。
def single_hashable(li):
existed = set()
for x in li:
if x not in existed:
yield x
existed.add(x)
assert list(single_hashable([1,2,4,2,4,3])) == [1,2,4,3]
“”"
每日一题:删除list 里面的重复元素 并保持顺序不变化
例 [1,2,3,2,4,3] 变成 [1,2,3,4]
“”"
alist = [1, 5, 2, 3, 5, 3, 2, 4, 3, 6]
blist =
for i in alist:
if i in blist:
pass
else:
blist.append(i)
print(blist)
lst_1 = [1,2,4,2,4,3]
lst_2 =
for i in lst_1:
if i not in lst_2:
lst_2.append(i)
print(lst_2)
def func2(sss):
#用字典result,将元素放入key(key不能重复)
result = { i:'a' for i in sss }
list_1 = result.keys()
return list(list_1)
print(func2([1, 3, 2, 2, 3, 5, 5, 4, 4]))a=[1,2,4,2,4,3]
b=list(set(a))
b.sort(key=a.index)
print(b)
def delItem(a,b={}):
for item in a :
if item not in b.keys():
b[item] = a.count(item)
return list(b.keys())
assert delItem([1, 2, 4, 2, 4, 3]) == [1,2,4,3]
def solution(nums: list) -> list:
# your code here
result = []
for i in nums:
if i not in result:
result.append(i)
return result
assert solution([1,2,4,2,4,3]) == [1,2,4,3]
def solution(num:list)->list:
new_num = []
for i in num:
if i not in new_num:
new_num.append(i)
return new_num
def solve(test_list: list):
result = []
for i in test_list:
if i not in result:
result.append(i)
return result
assert solve([1, 2, 4, 2, 4, 3]) == [1, 2, 4, 3]
assert solve([1, 2, 2, 2, 2, 1]) == [1, 2]
assert solve([]) == []
def solution(a:list)->list:
res_list=[]
for i in range(len(a)):
if a[i] not in res_list:
res_list.append(a[i])
return res_list
assert solution([1,2,4,2,4,3])==[1,2,4,3]
def test_list_info():
list_a=[1,2,4,2,4,3]
new_list=[]
for i in list_a:
if i not in new_list:
new_list.append(i)
print(new_list)
class DelectSameElement:
# 初始化定义列表
def init(self,l):
self.l = l
# 列表转成字典后,取keys再转成列表
def remove_same_elements1(self):
# 新建空字典
dict1 = {}
# 遍历列表,新增字典的元素
for i in self.l:
dict1[i] = i
# 返回字典的keys强转list
return list(dict1.keys())
def remove_same_elements2(self):
# 新建空列表
nl=[]
# 遍历列表
for i in range(len(self.l)):
# 如果元素不在新列表中
if self.l[i] not in nl:
# 新列表新增该元素
nl.append(self.l[i])
# 返回新列表
return nl
# 强转字典后再强转列表,用dict.fromkeys()方法
def remove_same_elements3(self):
return list(dict.fromkeys(self.l))