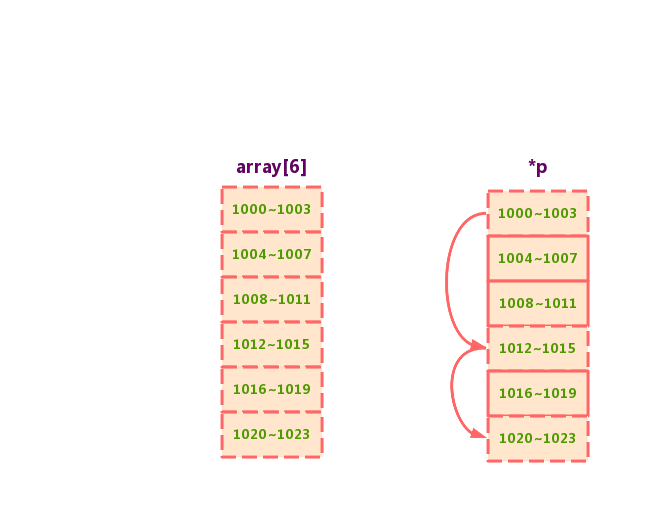
链表与数组的区别
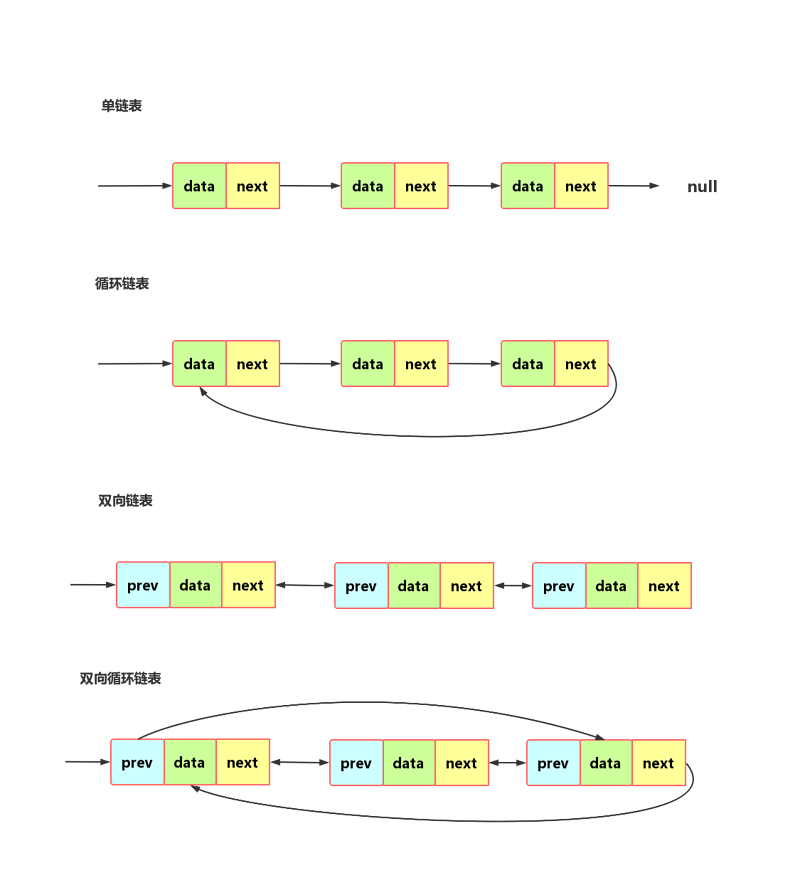
单链表与循环链表
注意链表中的头结点和尾结点。
循环链表从尾可以方便的到头,适合环型结构数据,比如约瑟夫问题。
双向链表
优势:
O(1) 时间复杂度找到前驱结点
删除,插入更高效。考虑以下两种情况:
- 删除结点中“值等于某个给定值”的结点
- 删除给定指针指向的结点
查询更高效:记录上次查找的位置 p,每次查询时,根据要查找的值与 p 的大小关系,决定是往前还是往后查找,所以平均只需要查找一半的数据。
再次比较数组和链表
从复杂度分析:
| 时间复杂度 | 数组 | 链表 |
|---|---|---|
| 插入删除 | O(n) | O(1) |
| 随机访问 | O(1) | O(n) |
其它角度:
-
内存连续,利用 CPU 的缓存机制,预读数组中的数据,所以访问效率更高。
-
而链表在内存中并不是连续存储,所以对 CPU 缓存不友好,没办法有效预读。
-
数组的大小固定,即使动态申请,也需要拷贝数据,费时费力。
-
链表支持动态扩容.
public class SinglyLinkedList {
Node head;
public void insertTail(int value) {
if (head == null) {
insertToHead(value);
return;
}
Node q = head;
while (q.next != null) {
q = q.next;
}
Node newNode = new Node(value);
q.next = newNode;
}
public void insertToHead(int value) {
Node newNode = new Node(value);
newNode.next = head;
head = newNode;
}
public boolean deleteByValue(int value) {
if (head == null)
return false;
Node p = head;
Node q = null;
while (p != null && p.data != value) {
q = p;
p = p.next;
}
// 链表中,没有 value
if (p == null)
return false;
// 数据在 head 上
if (q == null) {
head = head.next;
} else {
q.next = p.next;
}
return true;
}
public Node findByValue(int value) {
if (head == null)
return null;
Node q = head;
while (q != null && q.data != value) {
q = q.next;
}
if (q == null)
return null;
return q;
}
public void insertAfter(Node node, int value) {
if (node == null)
return;
Node newNode = new Node(value);
newNode.next = node.next;
node.next = newNode;
}
public void insertBefore(Node node, int value) {
if (node == null)
return;
if (head == null) {
insertToHead(value);
} else {
Node q = head;
while (q != null && q.next != node) {
q = q.next;
}
if (q == null)
return;
Node newNode = new Node(value);
newNode.next = q.next;
q.next = newNode;
}
}
public void printAll() {
if (head == null)
return;
Node q = head;
while (q != null) {
System.out.print(q.data + " ");
q = q.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
public static class Node {
int data;
Node next;
public Node(int data) {
this.data = data;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
SinglyLinkedList link = new SinglyLinkedList();
int data[] = { 1, 2, 5, 3, 1 };
for (int i = 0; i < data.length; i++) {
link.insertTail(data[i]);
}
link.insertToHead(99);
// 打印内容为 99 1 2 5 3 1
link.printAll();
link.deleteByValue(2);
System.out.println(!link.deleteByValue(999));
System.out.println(link.deleteByValue(99));
// 打印内容为 1 5 3 1
link.printAll();
System.out.println(link.findByValue(2) == null);
Node newNode = link.findByValue(3);
link.insertAfter(newNode, 10);
System.out.println(link.findByValue(3).next.data == 10);
link.insertBefore(newNode, 30);
System.out.println(link.findByValue(5).next.data == 30);
}
}