点击上方蓝字关注我们!
背景
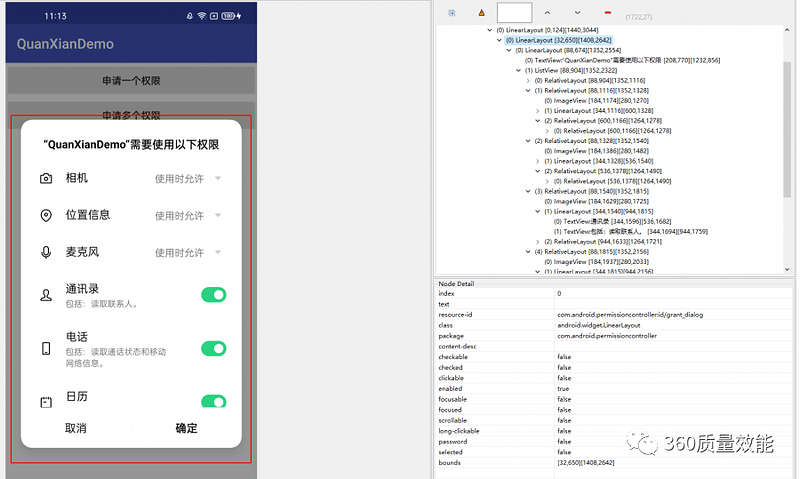
在Android UI遍历测试中,除传统的基于monkey的随机性测试外,基于模型的测试在测试覆盖率和可回溯性上表现更好,是目前热门的研究方向。在基于模型的测试中,对UI页面的定义和动作事件的筛选是十分重要而基础的工作。本文将介绍UI页面定义和动作事件筛选的具体方法。
技术实现
本项目使用python。我们可以使用UI Automator来获取UI界面的层次树信息。
01
View Tree
UI页面其实是一种树状结构的数据,称作view tree,其节点是每一个子view。每个子view一般包含’resource_id’、‘scrollable’、‘clickable’、'bounds’等信息,我们可以充分利用这些信息,来对页面进行定义以及动作事件的筛选。
为了便于操作,先将view tree树结构转成list列表形式,并保存子view的index索引等信息。
def get_view_list(view_tree):
view_tree['parent'] = -1
view_list = []
view_tree_to_list(0, view_tree, view_list)
self.last_acc_event['view_list'] = view_list
return view_list
def view_tree_to_list(index, view_tree, view_list):
tree_id = len(view_list)
view_tree['temp_id'] = tree_id
bounds = [[-1, -1], [-1, -1]]
bounds[0][0] = view_tree['bounds'][0]
bounds[0][1] = view_tree['bounds'][1]
bounds[1][0] = view_tree['bounds'][2]
bounds[1][1] = view_tree['bounds'][3]
width = bounds[1][0] - bounds[0][0]
height = bounds[1][1] - bounds[0][1]
view_tree['size'] = "%d*%d" % (width, height)
view_tree['index'] = index
view_tree['bounds'] = bounds
view_list.append(view_tree)
children_ids = []
for item in range(len(view_tree['children'])):
child_tree = view_tree['children'][item]
child_tree['parent'] = tree_id
view_tree_to_list(item, child_tree, view_list)
children_ids.append(child_tree['temp_id'])
view_tree['children'] = children_ids
02
新页面的定义
def get_state_str(view_list):
state_str_raw = get_state_str_raw(view_list)
return md5(state_str_raw)
def get_state_str_raw(view_list):
view_signatures = set()
for view in view_list:
view_signature = get_view_signature(view)
if view_signature:
view_signatures.add(view_signature)
return "%s{%s}" % (self.foreground_activity, ",".join(sorted(view_signatures)))
def get_view_signature(view_dict):
view_text = view_dict['text']
if view_text is None or len(view_text) > 50:
view_text = "None"
signature = "[class]%s[text]%s[%s,%s,%s,%s]" % \
(view_dict['class'],
view_text,
view_dict['clickable'],
view_dict['checked'],
view_dict['scrollable'],
view_dict['long-clickable']
)
return signature
03
动作事件筛选
我们遍历所有的子view,首先去掉’resource_id’为’android:id/navigationBarBackground’、'android:id/statusBarBackground’的导航栏的view,这在遍历测试中是不需要的。但有的app,它的导航栏view的’resource_id’不是这个,那就需要新加入过滤的内容,或者直接通过顶栏的坐标过滤掉导航栏。
def get_possible_input(view_list):
possible_events = []
enabled_view_ids = []
touch_exclude_view_ids = set()
for view_dict in view_list:
if view_dict['enabled'] and \
view_dict['resource_id'] not in \
['android:id/navigationBarBackground',
'android:id/statusBarBackground']:
enabled_view_ids.append(view_dict['temp_id'])
for view_id in enabled_view_ids:
if view_list[view_id]['scrollable']:
possible_events.append(ScrollEvent(view=views_list[view_id], direction="UP"))
possible_events.append(ScrollEvent(view=views_list[view_id], direction="DOWN"))
possible_events.append(ScrollEvent(view=views_list[view_id], direction="LEFT"))
possible_events.append(ScrollEvent(view=views_list[view_id], direction="RIGHT"))
elif view_list[view_id]['clickable']:
possible_events.append(TouchEvent(view=views_list[view_id]))
touch_exclude_view_ids.add(view_id)
# elif views_list[view_id]['enabled'] and \
# views_list[view_id]['focusable']:
# possible_events.append(TouchEvent(view=views_list[view_id]))
return possible_events
for view_id in enabled_view_ids:
if views_list[view_id]['scrollable']:
possible_events.append(ScrollEvent(view=views_list[view_id], direction="UP"))
# possible_events.append(ScrollEvent(view=views_list[view_id], direction="DOWN"))
possible_events.append(ScrollEvent(view=views_list[view_id], direction="LEFT"))
possible_events.append(ScrollEvent(view=views_list[view_id], direction="RIGHT"))
for view_id in enabled_view_ids:
if views_list[view_id]['clickable']:
possible_events.append(TouchEvent(view=views_list[view_id]))
touch_exclude_view_ids.add(view_id)
def filter_possible_input(possible_events,origin_dim=[1080, 1920]):
filter_events = []
for event in possible_events:
# 过滤坐标为负的值
bounds = event.view["bounds"]
bounds = [bounds[0][0], bounds[0][1], bounds[1][0], bounds[1][1]]
x_min = max(0, bounds[0])
y_min = max(0, bounds[1])
x_max = min(origin_dim[0], bounds[2])
y_max = min(origin_dim[1], bounds[3])
if x_min >= x_max or y_min >= y_max:
continue
# 更新bounds坐标点
event.view["bounds"] = [[x_min,y_min],[x_max,y_max]]
# 过滤小于5个像素的event
if (y_max-y_min) < 5:
pass
else:
filter_events.append(event)
return filter_events
总结
通过对页面的定义和动作事件的筛选,我们可以将不同的页面进行区分,相似的页面归为一类,筛选有效的event事件。在此基础上,我们可以构建图模型,将测试任务变为对有向图的遍历问题,在图模型上应用不同的算法,比如深度优先遍历、启发式搜索、深度学习或者强化学习算法等,对App进行充分的遍历测试。