前言
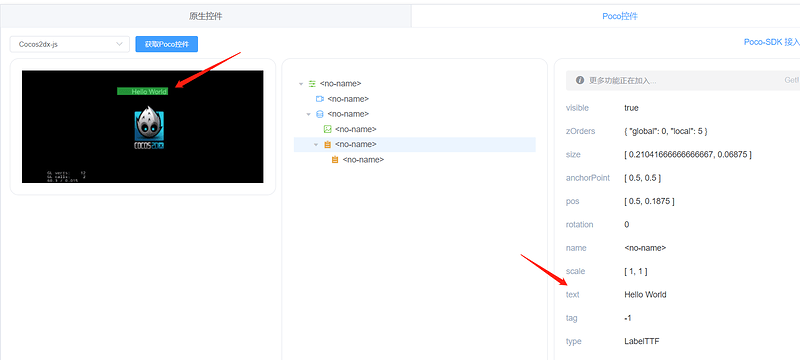
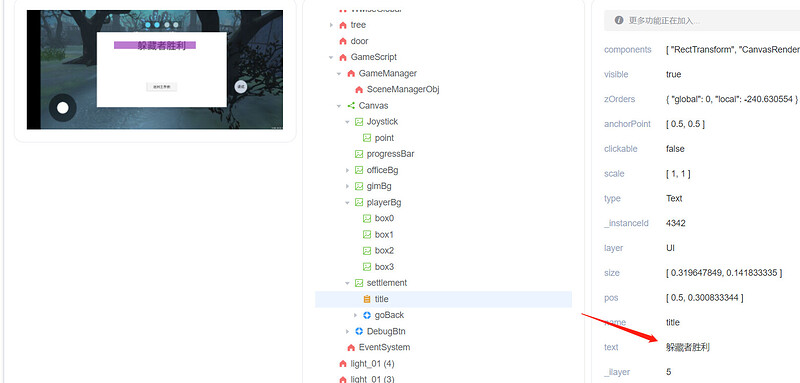
效果展示
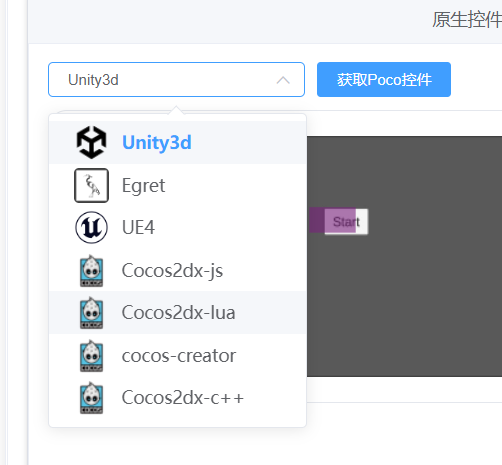
目前已支持POCO-SDK的所有游戏引擎(Unity3d、Cocos2dx系列、白鹭、UE4),使用前需游戏已接入SDK。v1.4.0-beta更新后就可以使用啦~ (预计五一后更新)
什么是POCO
Poco 是一个基于 UI 控件搜索的跨引擎自动化测试框架。支持主流游戏引擎:Cocos2d-x、Unity3d、安卓原生应用
https://poco-chinese.readthedocs.io/en/latest/
实现过程
以往获取poco控件更多是使用Airtest框架的python client或者Airtest IDE去获取,但是Sonic是Java为后端主要开发语言,仅获取控件而引入python环境就显得浪费,于是尝试从SDK层面去寻找答案。SDK github
以Unity3d为例:
PocoManager.cs
我们从这个文件可以看到SDK暴露的TCPServer是RPC协议,暴露的方法有:
rpc = new RPCParser();
rpc.addRpcMethod("isVRSupported", vr_support.isVRSupported);
rpc.addRpcMethod("hasMovementFinished", vr_support.IsQueueEmpty);
rpc.addRpcMethod("RotateObject", vr_support.RotateObject);
rpc.addRpcMethod("ObjectLookAt", vr_support.ObjectLookAt);
rpc.addRpcMethod("Screenshot", Screenshot);
rpc.addRpcMethod("GetScreenSize", GetScreenSize);
rpc.addRpcMethod("Dump", Dump);
rpc.addRpcMethod("GetDebugProfilingData", GetDebugProfilingData);
rpc.addRpcMethod("SetText", SetText);
rpc.addRpcMethod("GetSDKVersion", GetSDKVersion);
很明显,Dump方法就是我们需要的。
话不多说,服务端开搞。
// Call a method in the server
public string formatRequest(string method, object idAction, List<object> param = null)
{
Dictionary<string, object> data = new Dictionary<string, object>();
data["jsonrpc"] = "2.0";
data["method"] = method;
if (param != null)
{
data["params"] = JsonConvert.SerializeObject(param, settings);
}
// if idAction is null, it is a notification
if (idAction != null)
{
data["id"] = idAction;
}
return JsonConvert.SerializeObject(data, settings);
}
从这里得知,TCPServer是获取这个请求体,然后根据method字段映射到不同方法。
// Send a response from a request the server made to this client
public string formatResponse(object idAction, object result)
{
Dictionary<string, object> rpc = new Dictionary<string, object>();
rpc["jsonrpc"] = "2.0";
rpc["id"] = idAction;
rpc["result"] = result;
return JsonConvert.SerializeObject(rpc, settings);
}
返回时的id便是请求的id一一对应,然后result就是对应方法的返回内容,我们需要的信息就在这里面提取。
具体通信细节
我们从这里得知TcpServer.cs
public class SimpleProtocolFilter : ProtoFilter
{
/* 简单协议过滤器
协议按照 [有效数据字节数][有效数据] 这种协议包的格式进行打包和解包
[有效数据字节数]长度HEADER_SIZE字节
[有效数据]长度有效数据字节数字节
本类按照这种方式,顺序从数据流中取出数据进行拼接,一旦接收完一个完整的协议包,就会将协议包返回
[有效数据]字段接收到后会按照utf-8进行解码,因为在传输过程中是用utf-8进行编码的
所有编解码的操作在该类中完成
*/
private byte[] buf = new byte[0];
private int HEADER_SIZE = 4;
private List<string> msgs = new List<string>();
public void input(byte[] data)
{
buf = Combine(buf, data);
while (buf.Length > HEADER_SIZE)
{
int data_size = BitConverter.ToInt32(buf, 0);
if (buf.Length >= data_size + HEADER_SIZE)
{
byte[] data_body = Slice(buf, HEADER_SIZE, data_size + HEADER_SIZE);
string content = System.Text.Encoding.Default.GetString(data_body);
msgs.Add(content);
buf = Slice(buf, data_size + HEADER_SIZE, buf.Length);
}
else
{
break;
}
}
}
public byte[] pack(String content)
{
int len = content.Length;
byte[] size = BitConverter.GetBytes(len);
if (!BitConverter.IsLittleEndian)
{
//reverse it so we get little endian.
Array.Reverse(size);
}
byte[] body = System.Text.Encoding.Default.GetBytes(content);
byte[] ret = Combine(size, body);
return ret;
}
无论是发消息或是收消息,都是将消息体的长度作为head先发送一次,再发送请求体。收消息时同理。
Sonic通信如下:
poco = new Socket("localhost", port);
inputStream = poco.getInputStream();
outputStream = poco.getOutputStream();
int len = jsonObject.toJSONString().length();
ByteBuffer header = ByteBuffer.allocate(4);
header.put(BytesTool.intToByteArray(len), 0, 4);
header.flip();
ByteBuffer body = ByteBuffer.allocate(len);
body.put(jsonObject.toJSONString().getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8), 0, len);
body.flip();
ByteBuffer total = ByteBuffer.allocate(len + 4);
total.put(header.array());
total.put(body.array());
total.flip();
outputStream.write(total.array());
过程总结
那么总结一下,其实通信过程没有想象复杂。
- 第一步是拼接我们需要的请求体。
JSONObject jsonObject = new JSONObject();
jsonObject.put("jsonrpc", "2.0");
jsonObject.put("params", Arrays.asList(true));
jsonObject.put("id", UUID.randomUUID().toString());
jsonObject.put("method", "Dump");
//部分引擎为小写dump
- 根据协议规则发送给Socket
- 接收信息
while (poco.isConnected() && !Thread.interrupted()) {
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];
int realLen;
realLen = inputStream.read(buffer);
if (buffer.length != realLen && realLen >= 0) {
buffer = subByteArray(buffer, 0, realLen);
}
if (realLen >= 0) {
s.append(new String(buffer));
if (s.toString().getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8).length == headLen) {
result.set(s.toString());
break;
}
}
}
- 将结果发送给前端解析
- 兼容不同引擎协议,有的引擎是走websocket特殊兼容一下。
结语
POCO是用户呼声很高的一个需求,目前功能只是获取游戏控件,后续会利用POCO做更多游戏自动化上的工作。也感谢大家一直关注Sonic。